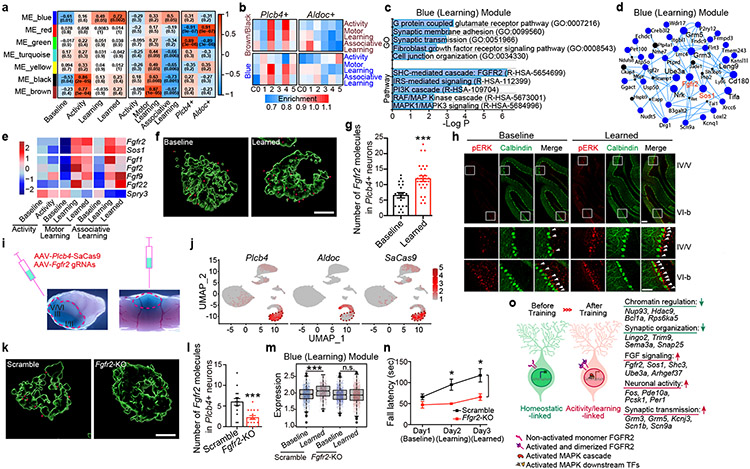
Figure 4. FGFR2 signaling in Plcb4+ Purkinje neurons is required for learning-dependent transcription and motor learning.
(a) Module-trait correlation analysis. (b) Enrichment of learning and activity module genes in Plcb4+ or Aldoc+ neuron clusters. (c) Gene Ontology and Pathway analyses of the blue module genes. (d) Hub-gene network analysis of the blue module genes. (e) Average gene expression under different conditions, presented as normalized Z-scores. (f) RNA ISH analyses of Fgfr2 mRNA in Plcb4+ neurons. Scale bar, 5μm. (g) The number of Fgfr2 positive signals per Plcb4+ Purkinje neuron, presented as mean ± s.e.m, ***p=0.0002, n=20 (baseline) and 28 (learned) Plcb4+ neurons from 5 mice, two-tailed t-test. (h) Representative images of pERK and Calbindin in lobules IV/V and VI-b in sagittal cerebellar sections. Scale bars, 100 μm (upper panel) and 50 μm (lower panel). (i) Stereotaxic injection of AAV-Plcb4-SaCas9 and AAV-Fgfr2 gRNAs into the anterior vermis. (j) FeaturePlot showing the co-localization of SaCas9 with Plcb4, but not with Aldoc. (k) ISH of Fgfr2 mRNA in Plcb4+ neurons two weeks following CRISPR-induced knockout or control. Scale bar, 5μm. (l) Number of Fgfr2 positive signals per Plcb4+ neuron is presented as mean ± s.e.m, ***p=0.0004, n=15 Plcb4+ Purkinje neurons from 3 mice, two-tailed t-test. (m) Blue module genes were reduced upon Fgfr2 knockout in Plcb4+ cells. ***p=1.42e-09 for scramble in Plcb4+ neurons, two-sided un-paired t-test. n=2 in biologically independent snRNA-seq. 977 and 637 nuclei in scramble baseline and learned samples. 974 and 1514 nulcei in Fgfr2-KO baseline and learned samples. (n) Fall latency from mice upon Fgfr2 knockout in Plcb4+ neurons or control is presented as mean ± s.e.m. *p=0.018, 0.021 for days 2-3, n=6 mice, ANOVA followed by Fisher's PLSD post hoc test. (o) A model of Plcb4+ Purkinje neurons from baseline to activity/learning-linked state.