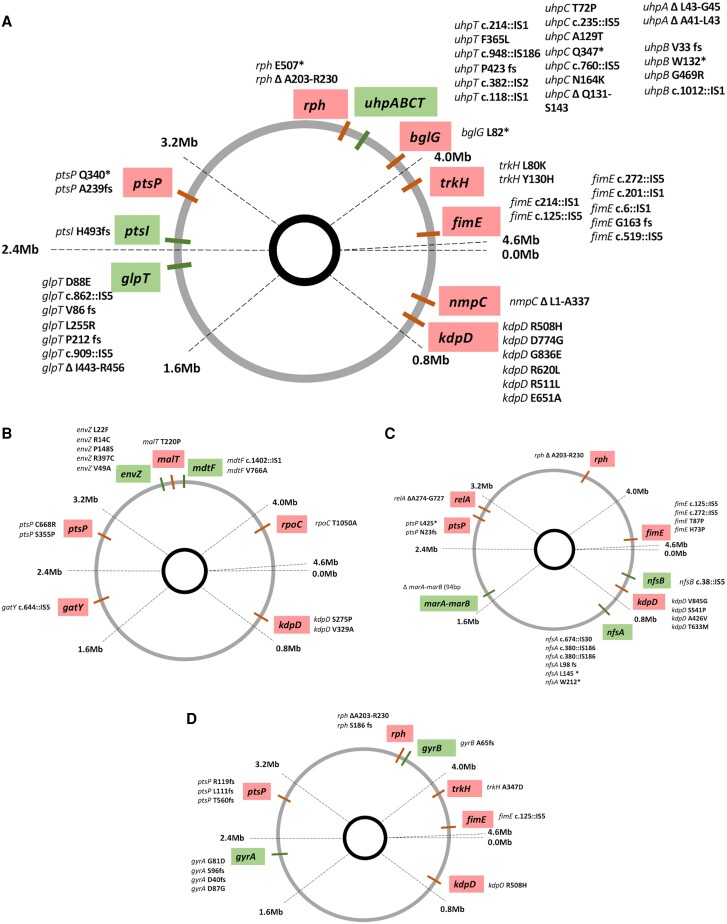
Fig. 8.
Unique mutations contribute to the increase in resistance and growth environment adaptation. Whole-genome sequencing of multiple clones identified 95 unique mutations across 24 genes that potentially contribute to either an increase in resistance (marked as green) or adaptation to the growth (non-antibiotic) environment (marked as red). These are individually shown for each antibiotic (A-fosfomycin, B-tetracycline, C-nitrofurantoin, and D-ciprofloxacin). The mutations observed in the different mutants are listed next to each gene.