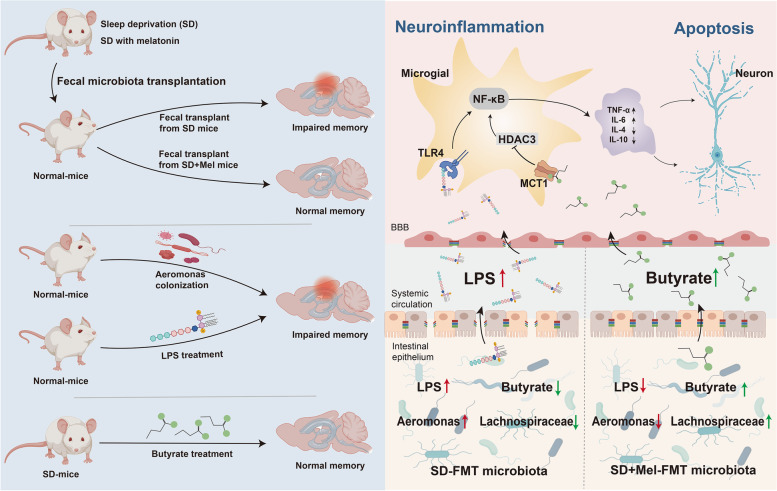
Fig. 11.
Schematic diagram of the protective effects of melatonin on cognitive impairment caused by sleep deprivation through the microbiota–gut–brain axis. Briefly, gut microbes and their metabolites mediate the ameliorative effect of melatonin on SD-induced cognitive impairment. A feasible mechanism is that Mel downregulates the Aeromonas population and production of the constituent LPS production and upregulates the Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136 population and the production of the butyrate metabolite by remodeling gut microbiota homeostasis. These events inhibit the TLR4/HDAC3/NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby preventing neuroinflammation and ultimately alleviating neuronal apoptosis and memory impairment in sleep-deprived mice. HDAC3: histone deacetylase3, LPS: lipopolysaccharide, Mel: melatonin, NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB, SD: sleep deprivation, TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4