Fig. 2 |. Common spatial transcriptomics techniques.
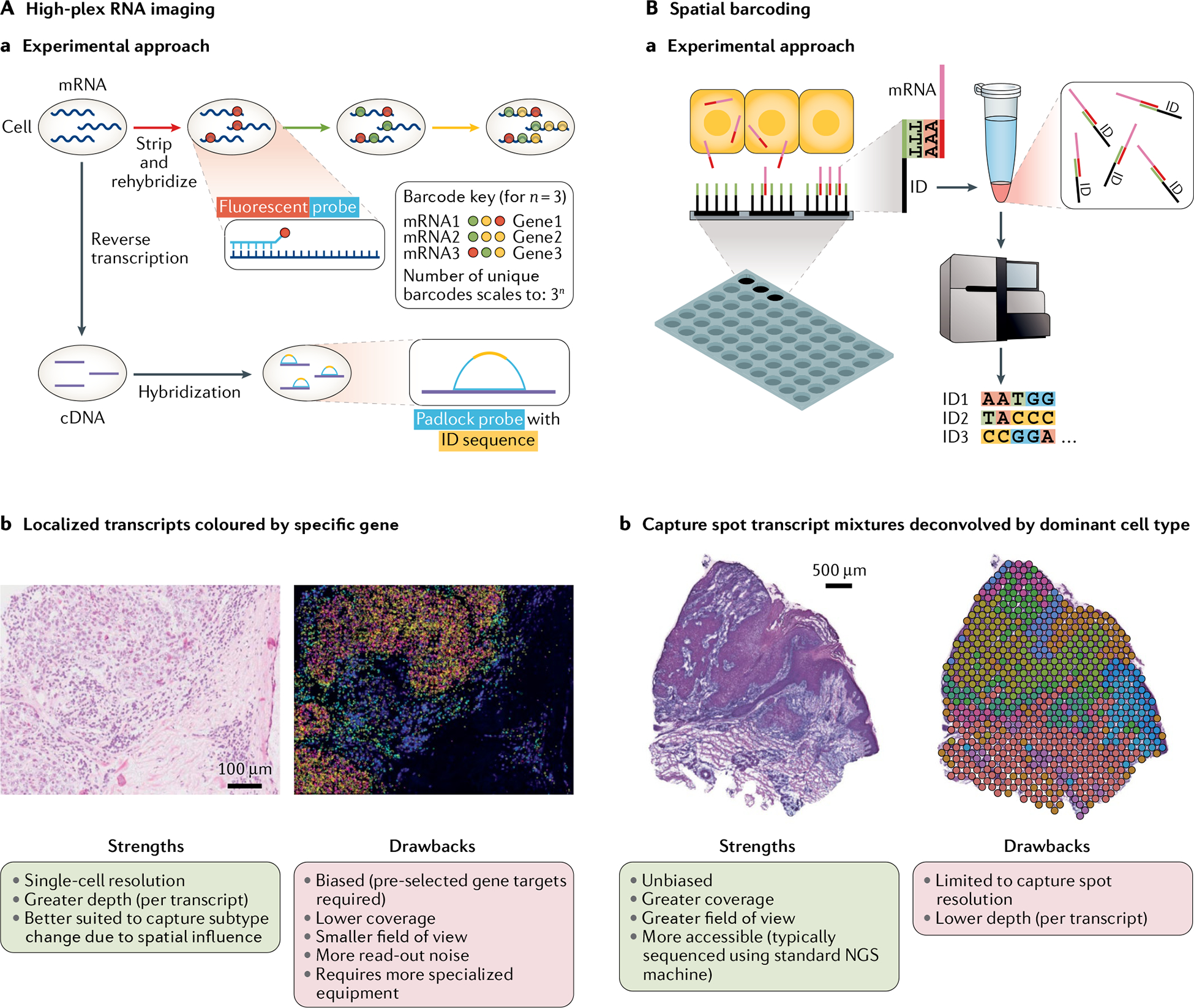
Aa | High-plex RNA imaging (HPRI) methods localize mRNA transcripts through probes that target specific genes. Fluorescent probe methods typically employ an encoding scheme whereby each gene can be identified through a unique sequence of fluorescent probe signals obtained through multiple rounds of hybridization. Padlock probe methods typically use probes that target the complementary DNA (cDNA) of target genes. Each probe has an identification (ID) sequence of nucleotides specific to each gene. The strategy for fluororescent sequencing of this ID varies by method. Ab | HPRI map of human breast cancer tissue cross-section with mRNA transcripts decoded based on gene fluorescent signals (not yet annotated by cell type, which can be done through mapping). Left: associated haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain (scale bar = 100 μm). Strengths and drawbacks of HPRI methods are listed. Pre-selected gene target panels typically range from 100 to 200 genes for intact tissue sections (proof-of-concept literature indicates an ~10,000 gene limit in tissue culture that is not easily scaled to intact tissue), and for some well-established methods only long RNA species (greater than 1,000 nucleotides) can be included. More specialized equipment typically makes for a more labour-intensive workflow. Ba | Spatial barcoding uses spatially barcoded (ID = location barcode) poly-T oligonucleotide capture of mRNA transcripts across tissue cross-sections followed by detachment and deep sequencing. Following sequencing, each transcript is de-multiplexed for assignment to its capture spot of origin based on its ID. Bb | Spatial barcoding map of human squamous cell carcinoma cross-section with capture spot mRNA mixtures deconvolved by cell type. Left: associated H&E stain (scale bar = 500 μm). Strengths and drawbacks of spatial barcoding methods are listed. Unbiased refers to the fact that the method does not involve selection of target genes. Greater accessibility also comes from the commercialization of spatial barcoding methods. NGS, next-generation sequencing. Part Ab reprinted from REF.10, Springer Nature Limited.
