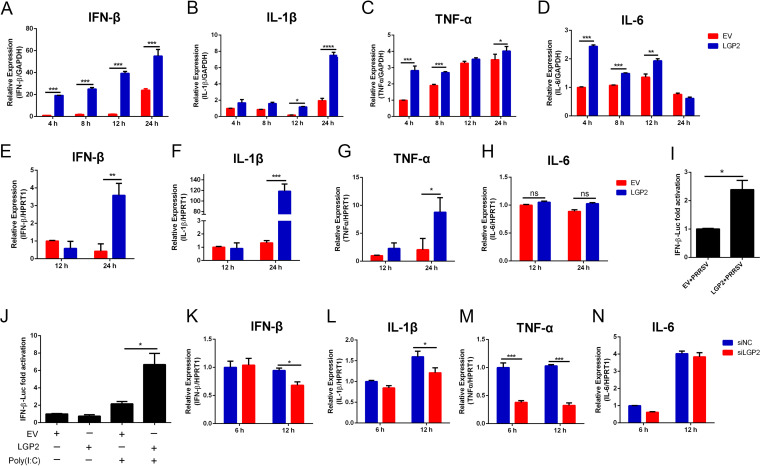
FIG 2.
LGP2 facilitates the expression of IFN-β and proinflammatory cytokines during PRRSV infection. (A to D) Marc-145 cells were transfected with control plasmid and LGP2 plasmid for 24 h, and cells were infected with PRRSV (MOI = 1) for 4, 8, 12, and 24 h. The relative expressions of IFN-β (A), IL-1β (B), TNF-α (C), and IL-6 (D) were detected using qRT-PCR, and GAPDH served as an internal control. (E to H) 3D4/21 cells were transfected with control plasmid and LGP2 plasmid for 24 h, and cells were infected with PRRSV (MOI = 1) for 12 and 24 h. The relative expression of IFN-β (E), IL-1β (F), TNF-α (G), and IL-6 (H) was detected using qRT-PCR. The data are normalized to GAPDH in each sample. (I) Marc-145 cells were transfected with the control plasmid and Myc-tagged LGP2 plasmid for 24 h, and cells were infected with PRRSV (MOI = 1). The activation of the IFN-β promoter was shown using dual-luciferase reporter assays. (J) HEK293T cells were mock stimulated or stimulated with poly(I·C) for 8 h in the absence or presence of LGP2 overexpression. The activation of the IFN-β promoter was shown using dual-luciferase reporter assays. (K to N) PAMs were transfected with negative-control siRNA or LGP2 siRNA (si-3) for 24 h and then infected with PRRSV (MOI = 1) for 6 and 12 h. The relative expression of IFN-β (K), IL-1β (L), TNF-α (M), and IL-6 (N) was detected using qRT-PCR. The data are normalized to GAPDH in each sample. The data are the results of three independent experiments (means ± the SE). Significant differences are denoted by asterisks (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).