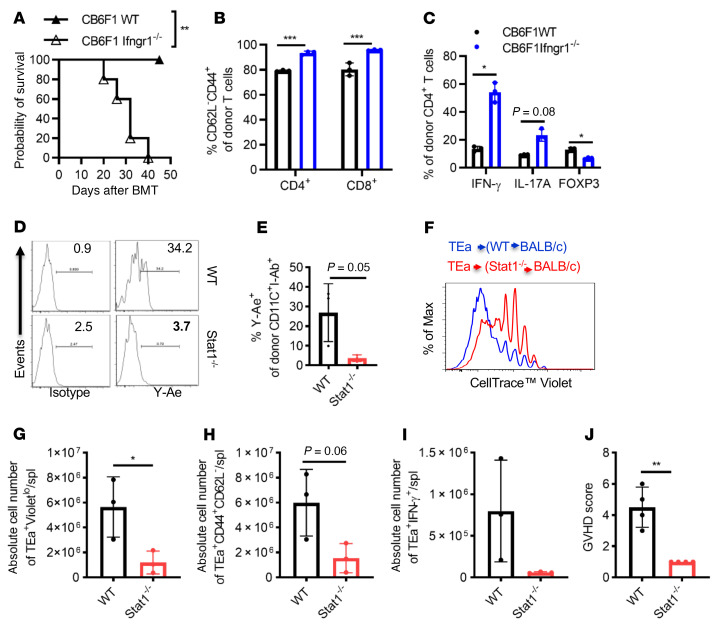
Figure 5. APCs with deficient IFN-γR/STAT1 signaling exhibit increased direct and compromised indirect antigen presentation.
(A) GVHD was induced in the P→F1 [B6.SJL(H2b)→CB6F1 (H2bxd)] mouse model using WT or Ifngr1–/– recipients, and GVHD-induced mortality was monitored. Ifngr1–/– F1 recipient mice exhibited significantly increased GVHD-induced mortality (MST of 32 days vs. not reached, log-rank test **P < 0.01, n = 5 mice/group). (B and C) Splenic T cell activation was determined by the percentage of CD62L–CD44+ donor T cells, and differentiation (Th1, Th17, and Treg) was assessed by IFN-γ, IL-17A, and FOXP3 expression in donor CD4+T cells on day 7 after BMT. n = 3 mice/group. (D and E) Donor-derived CD11c+ cells were assessed on day 18 after transplantation for MHC II (I-Ab) and associated Ea52-68 peptide presentation (Y-Ae expression) following fully MHC-mismatched BMT in BALB/c mice that received 5 × 106 TCD BMCs from either WT B6 or Stat1–/– mice after 8 Gy irradiation (n = 3 mice/group). (F–J) In vivo proliferation of TEa-TCR–Tg T cells specific for Ea52-68 peptide presented by I-Ab. Three weeks after transplantation, 5 × 106 CellTrace Violet–labeled pan–T cells from TEa-TCR–Tg mice were administered i.v. to B6.WT→BALB/c or B6.Stat1–/–→BALB/c chimeras. Proliferation was determined by CellTrace Violet dilution (F and G), activation (H), and Th1 differentiation (I) of antigen-specific TEa TCR+ donor T cells (CD4+Va2+Vb6+) on day 5 after DLI (n = 3 mice/group). (J) Clinical GVHD scores were recorded on day 7 after DLI of TEa-TCR–Tg T cells (n = 4 mice/group). Bar graphs represent the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, by 2-way ANOVA with Šidák’s correction (B and C) and 2-tailed Student’s t test (E and G–J).