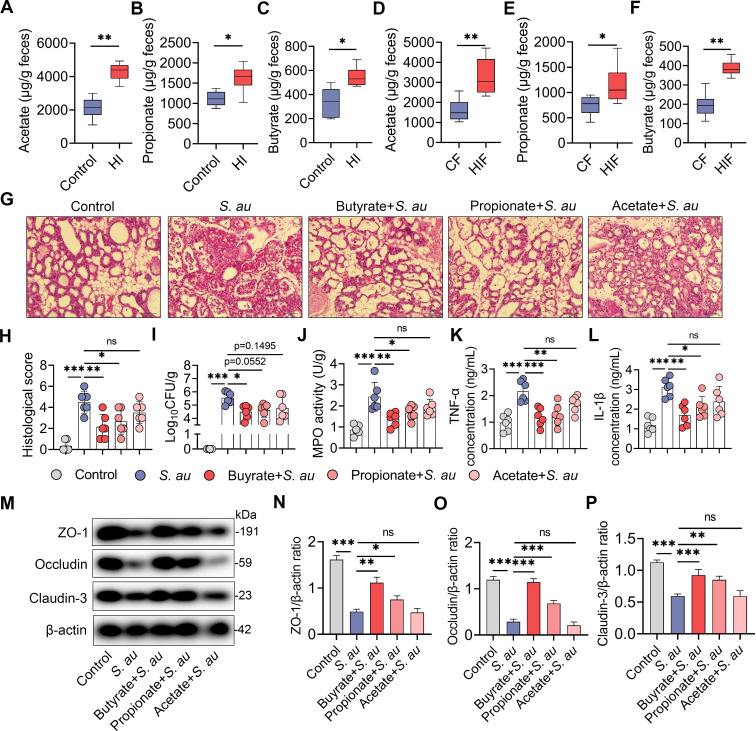
Fig 6. HI diet-derived SCFAs by gut microbiota metabolism alleviate S. au-induced mastitis in mice.
A-C. Fecal acetate (A), propionate (B) and butyrate (C) levels from control diet- and HI diet-treated mice (n = 6). D-F. Fecal acetate (D), propionate (E) and butyrate (F) levels from different FMT groups (n = 6). G-P. Mice were treated with 30 mg/kg butyrate, propionate and acetate for a week, followed by S. au-induced mastitis (n = 6). G. Representative H&E-stained images of the mammary glands from different treatment groups (scale bar, 50 μm). H. Histological score of the mammary gland based on H&E-stained sections (n = 6). I. Mammary S. au burden from the indicated groups (n = 6). J-L. Inflammatory markers, including MPO activity (J), TNF-α (K) and IL-β (L), from the indicated groups (n = 6). M. Representative images of mammary TJ proteins, including ZO-1, Occludin and Claudin-3, by western blotting. N-P. Relative intensity of TJ proteins including ZO-1 (N), Occludin (O) and Claudin-3 (P), using β-actin as an endogenous control. Data are presented as boxplots (A-F) or means ± SD (H-L and N-P). The Mann-Whitney U test (A-F) and one-way ANOVA (H-L and N-P) were performed for statistical analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 indicate significant differences.