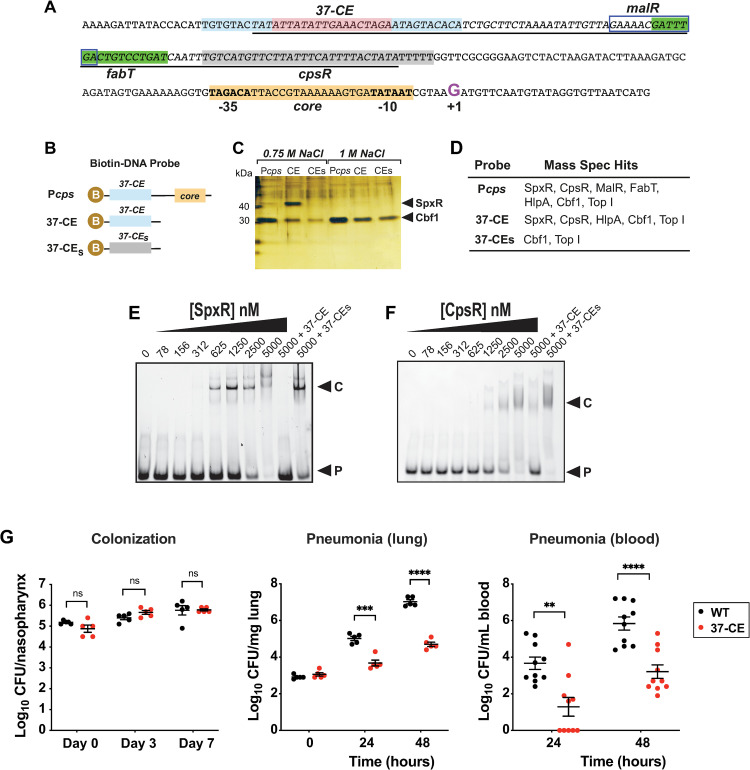
Fig 1. Identification and characterization of the 37-CE.
(A) Annotated Pcps sequence. The 37-CE is highlighted; the 10 bp perfect inverted repeat sequence is light blue while the 17 bp spacer region is pink. Proposed FabT and CpsR binding sites as identified in refs. (27) and (19, 26) are in green and grey, respectively. The proposed MalR binding site according to refs. (24, 25) is boxed. Core promoter elements are highlighted in orange. The Repeat Unit of Pneumococcus (RUP) sequence (34, 35), is underlined and the +1 transcriptional start site (G) is in purple. (B) Biotin (B) labelled DNA probes used to pull-down Pcps interacting partners. Pcps = full cps promoter; 37-CE = 37 bp cis element; 37-CEs = scrambled 37-CE sequence. (C) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE of biotin-conjugated DNA probe high salt eluates after bacterial lysate was bound and washed. SpxR and Cbf1 are indicated by the arrows. (D) Table of transcription factors identified using Mass Spectrometry (MS) by the three probes. (E) Representative EMSA of SpxR and (F) CpsR interaction with 37-CE double-stranded DNA probe. Excess unlabeled probe (+37-CE) or scrambled probe (+37-CEs) are used as controls. EMSAs were performed three times. (G) Murine infection studies. For colonization (left), mice were infected with 5x10^5 CFU and CFUs were determined on day 3 (5 mice/group) and day 7 (5 mice/group). For pneumonia, mice were infected with 5x10^6 CFU and CFUs were determined in lung homogenates (middle; 5 mice/group) and blood (right; 10 mice/group) at 24 and 48 hours post-infection. Individual data points, the mean and SEM are plotted. Statistical differences were determined using an unpaired t-test. Symbols: ns = not significant ***p≤0.001, ****p≤0.0001.