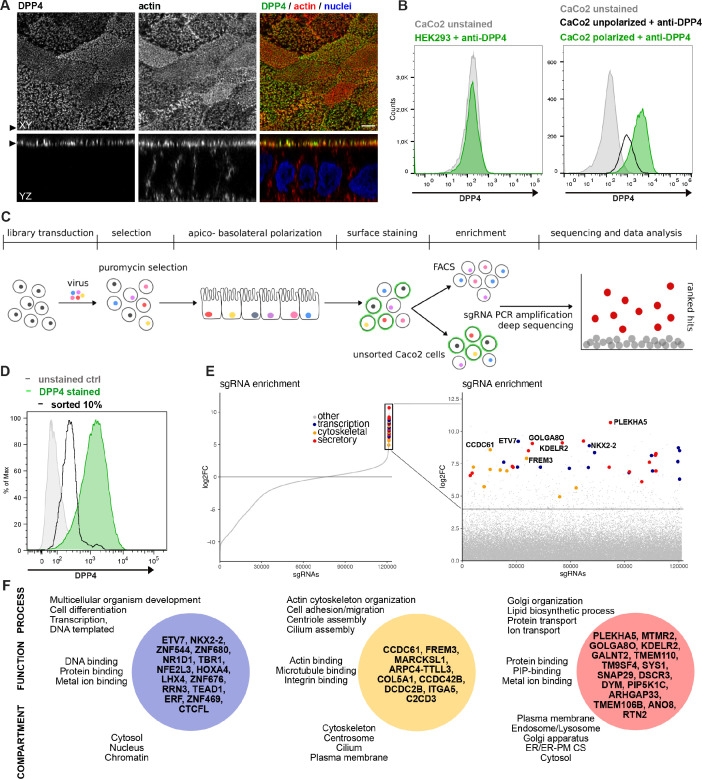
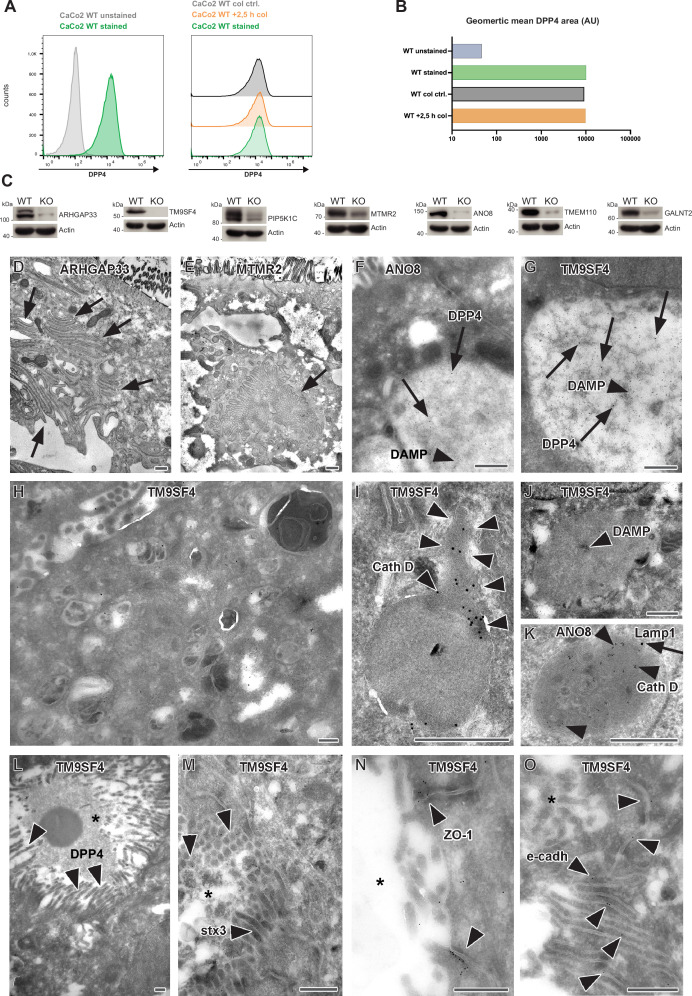
Figure 1. A CRISPR-mediated loss-of-function screen in polarized enterocytes.
(A) Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 (DPP4) localizes to the apical brush-border of polarized enterocytes and can be detected with a specific antibody at its extracellular stalk domain. Top view (XZ) and lateral view (YZ) of a polarized CaCo2 monolayer. Scale = 5 µm. (B) During polarization, apical DPP4 is increased due to polarized traffic and surface expansion, which can be measured by flow cytometry (right panel, CaCo2 unpolarized versus polarized). HEK293T cells, not expressing DPP4, serve as quality control for staining specificity. (C) CaCo2-Cas9 cells are transduced with the lentiGuide-Puro library and selected with puromycin. After selection, CaCo2 cells are seeded to confluent monolayers and cultured for apico-basolateral polarization. Subsequently, cells are detached, stained, and subjected to fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Sorted and unsorted control cells are processed for gDNA extraction and genomically integrated CRISPR constructs are amplified by PCR. Finally, PCR products of sorted and unsorted cell populations are analyzed by next-generation sequencing and sgRNAs are ranked by their enrichment in the sorted vs. unsorted cell polpulation. (D) Sorting was performed for 10% of the cells, with lowest surface-signal intensity, thereby enriching for the cell population that had lost 90% of surface DPP4 signal, due to efficient CRISPR targeting. (E) 89 single-guide RNAs were significantly enriched in the sorted cell population. (F) Factors enriched in the sorted cell population could functionally be associated with secretory traffic, cytoskeletal architecture, or transcription, in a manual gene -ontology analysis.