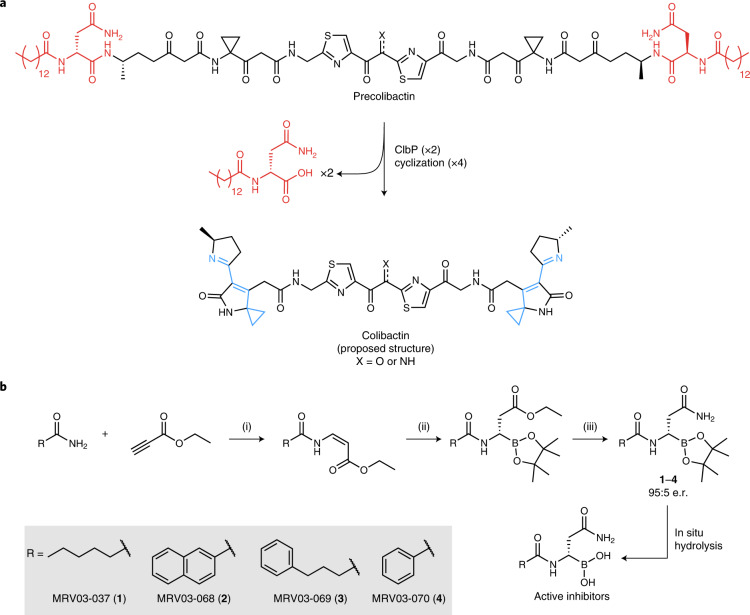
Fig. 1. Activity of ClbP guides rational design of colibactin biosynthesis inhibitors.
a, ClbP activates colibactin by removing an N-myristoyl-d-Asn prodrug scaffold (red). Hydrolysis of two amide bonds by ClbP leads to the formation of two electrophilic warheads (cyan) capable of DNA alkylation. Inhibitor design was guided by the two key recognition features of the prodrug scaffold: a d-Asn side chain, which is essential, and a lipid group, which can be modified. b, Synthesis of ClbP inhibitors: (i) Pd(OAc)2, NaOAc, trifluoroacetic acid, PhMe, 80 °C, 12 h; (ii) CuCl (0.1 equivalent), (R)-SEGPHOS (0.11 equivalent), bis(pinacolato)diboron (1.1 equivalents), KOt-Bu (1 equivalent), MeOH (4 equivalents), tetrahydrofuran, 3 h; (iii) NaCN (0.2 equivalent), NH3, MeOH, 1 h. e.r., enantiomeric ratio.