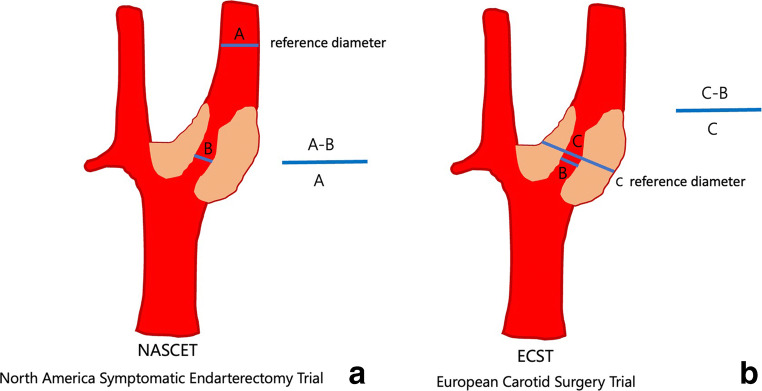
Fig. 1.
Measurement of carotid stenosis using the NASCET (a) and ECST (b) methods, revealing the difference in choice of reference diameters. While both methods use the narrowest luminal diameter at the location of stenosis, the reference diameter is in the NASCET method located well beyond the carotid bulb where the walls are parallel, while ESCT uses the outside diameter of the carotid bulb. All measurements are cross-sectional perpendicular to the long-axis of the artery, and expressed in percentage stenosis. As such, it is easy to understand that the same lesion leads to different degrees of stenosis between NASCET and ESCT. NASCET, North-America Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial; ESCT, European Carotid Surgery Trial