Fig. 3.
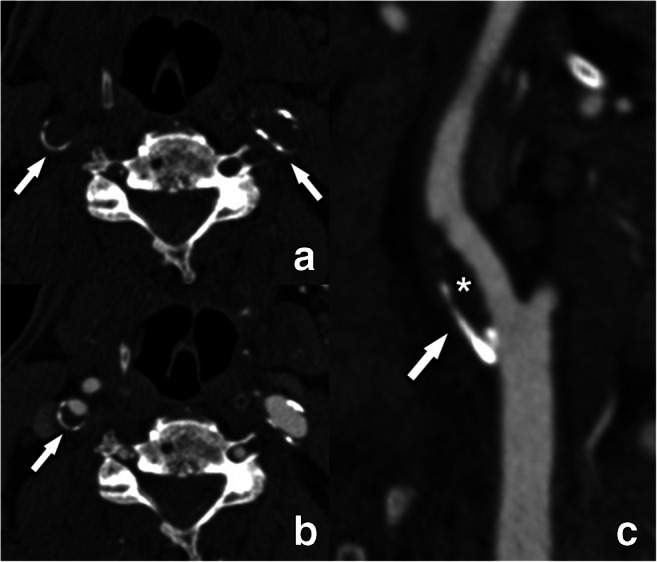
The rim sign illustrated on CT. Fine peripheral semicircular calcifications can be seen in both internal carotid arteries (arrows) on an unenhanced CT-scan at the level of the carotid bulb (a). After intravenous contrast (b and c), the plaque composition becomes more defined. The right internal carotid artery plaque is composed of a fine (< 2 mm thickness) semicircular adventitial calcification (arrow) and a more pronounced (> = 2mm thick) non-calcified component (asterisk), meeting the criteria for a so-called “rim sign.” The left internal carotid artery has small peripheral calcification of less than 2 mm thickness, but the non-calcified component is not large enough to qualify this plaque as a rim sign
