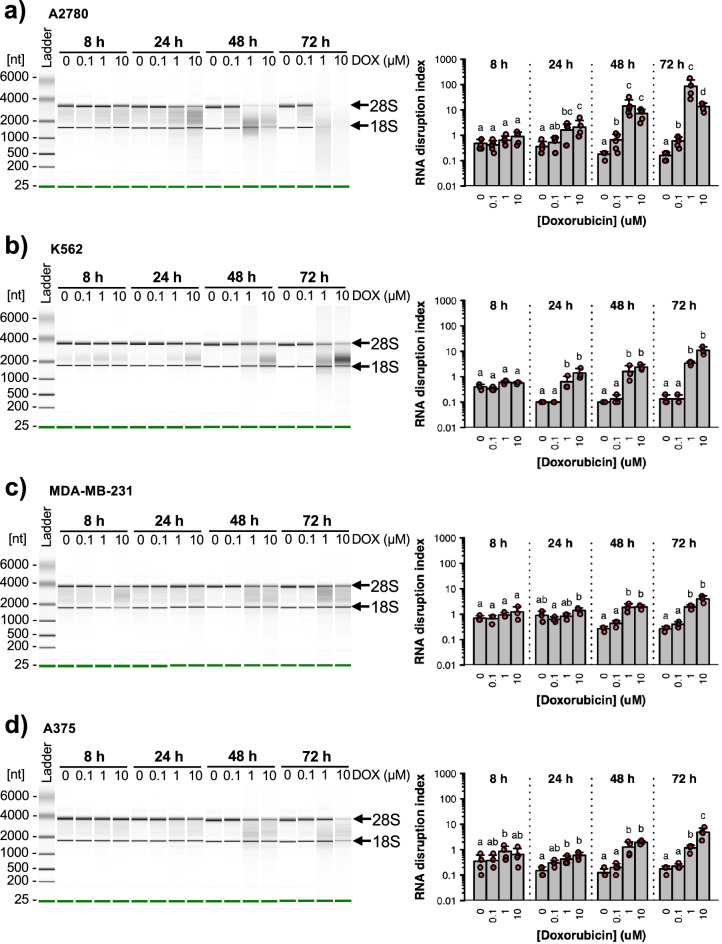
Figure 1.
Dose- and time-dependent RNA disruption in response to doxorubicin. A2780 (a), K562 (b), MDA-MB-231 (c) and A375 (d) cells were exposed to different concentrations of doxorubicin (DOX) for 8 to 72 h. Total RNA was isolated from cells following drug treatment, and RNA disruption was analyzed using the RDA. Left panels. Virtual gel images of total RNA isolated from doxorubicin-treated cells. Arrows indicate the position of the full-length 28S and 18S rRNA bands. Each electropherogram is representative of at least three independent biological replicates. Right panels. RNA disruption quantified using the RDA. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation, with individual data points shown in red. A two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction between drug concentration and treatment time for all four cell lines [A2780, F(9, 62) = 18.27, n = 4–5, P < 0.01; K562, F(9, 32) = 7.68, n = 3, P < 0.01; MDA-MB-231, F(9, 32) = 8.75, n = 3, P < 0.01; A375, F(9, 48) = 6.22, n = 4, P < 0.01]. For a given treatment time, group pairs labelled with the same letter are not significantly different.