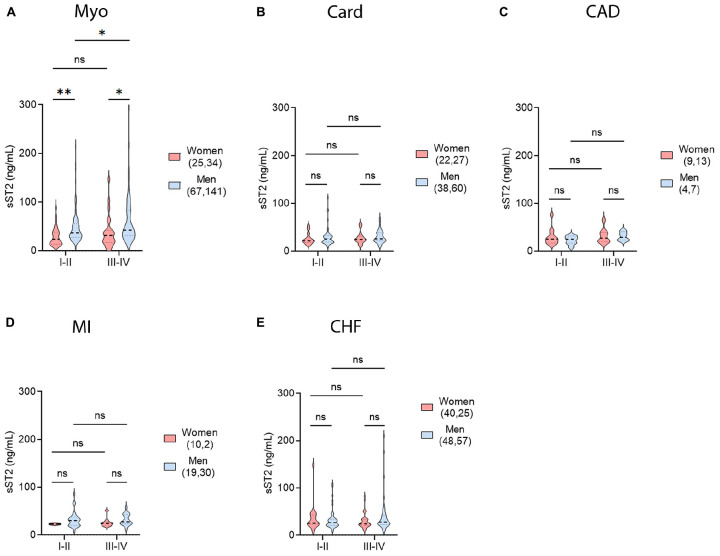
FIGURE 9.
Sex differences in NYHA class and sST2 levels. sST2 levels compared women and men (gray), women (peach), or men (blue) to New York Heart Association (NYHA) class I–II vs. III–IV heart failure for (A) myocarditis (Myo), (B) cardiomyopathy (Card), (C) coronary artery disease (CAD), (D) myocardial infarction (MI), or (E) congestive heart failure (CHF). Violin plots denote data distribution for each group. One-way ANOVA: (A) p = 0.0002, (B) p = 0.66, (C) p = 0.64, (D) p = 0.55, and (E) p = 0.28. (A) Two-way ANOVA p-values indicate no interaction between NYHA Class and sex (p = 0.59) in patients with myocarditis, but interactions between NYHA Class and sST2 (p = 0.04) and sex and sST2 (p = 0.0002). (B) Two-way ANOVA p-values indicate no interactions between NYHA Class and sex (p = 0.94), NYHA Class and sST2 (p = 0.74), or sex and sST2 (p = 0.22) in patients with cardiomyopathy. (C) Two-way ANOVA p-values indicate no interactions between NYHA Class and sex (p = 0.63), NYHA Class and sST2 (p = 0.32), or sex and sST2 (p = 0.52) in patients with CAD. (D) Two-way ANOVA p-values indicate no interactions between NYHA Class and sex (p = 0.75), NYHA Class and sST2 (p = 0.80), or sex and sST2 (p = 0.20) in patients with MI. (E) Two-way ANOVA p-values indicate no interactions between NYHA Class and sex (p = 0.12), NYHA Class and sST2 (p = 0.72), or sex and sST2 (p = 0.40) in patients with CHF. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.