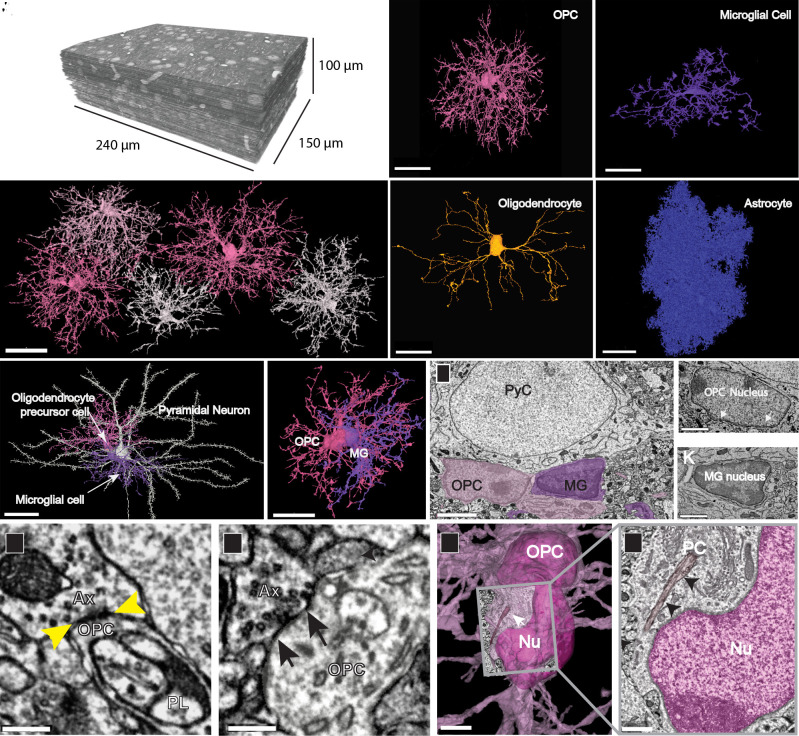
Fig. 1.
Distinct structural features of OPCs in the developing visual cortex. (A) TEM reconstruction of 100-µm3 volume of layer 2/3 mouse visual cortex (P36). (B) 3D reconstructions of a subset of OPCs in P36 dataset, showing discrete territories and tiling. (Scale bar, 30 µm.) (C) 3D rendering of an OPC from P36 dataset showing extensive ramifications emanating from the cell soma. (D) 3D rendering of a microglial cell shows its thicker, less branched processes and elongated and flattened soma. (E) 3D rendering of a mature myelinating oligodendrocyte in P36 dataset has a smooth and ovoid-shaped soma. Note, only the soma and cytoplasmic processes without myelin sheaths are shown. (F) 3D rendering of an astrocyte in P36 dataset showing its densely packed cytoplasmic protrusions. (Scale bars, C–F, 20 µm.) (G) 3D rendered pyramidal neuron (white) with an OPC (pink) and a microglial cell (MG, purple) both in satellite positions. (Scale bar, 30 µm.) (Movie S1) (H) 3D rendering of the same two glial cells in (G) shows their close association and intermingling of branches. (Scale bar, 20 µm.) (I) Ultrathin section slice through an OPC soma (pink) and microglial cell soma (purple). (Scale bar, 3 μm.) (J) Ultrathin section slice of an OPC nucleus with dense rim of heterochromatin and ruffled edge (white arrows). (Scale bar, 1.5 μm.) (K) Ultrathin section slice of a microglial nucleus showing its dense heterochromatin throughout. (Scale bar, 1.5 μm.) (L and M) Axons (Ax) making synaptic contacts (yellow and black arrows) with OPC processes. A phagolysosome (PL) is nearby in L. (Scale bar, 300 nm.) (N) The soma of an OPC (deep pink) bears a primary cilium (white arrow) adjacent to the nucleus (Nu). (Scale bar, 3 µm.) (O) Ultrathin slice of the boxed area in N showing the primary cilium (PC) (black arrows) close to the OPC nucleus (Nu, dark pink). (Scale bar, 750 nm.)