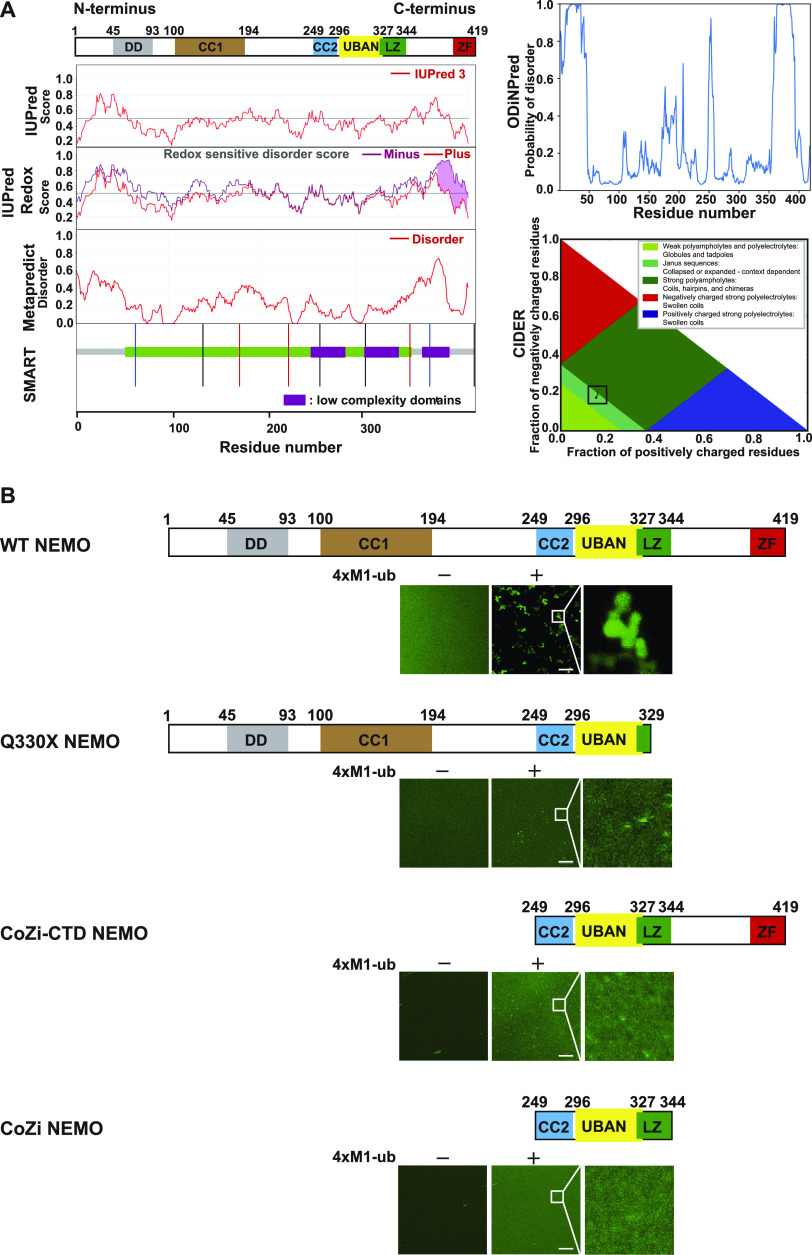
Figure 6. N- and C-terminal domains contribute to M1-ubiquitin–induced phase separation of NEMO.
(A) Bioinformatic analyses predicts IDRs in the N- and C-terminus of WT NEMO along with spanning low complexity domains. Schematic representation of the human NEMO domain structure is shown on top. DD, dimerization domain; CC, coiled coil; UBAN, ubiquitin binding in ABIN and NEMO; LZ, leucine zipper; ZF, zinc finger. The following bioinformatic tools were used: IUPred, prediction of intrinsically unstructured proteins; SMART, simple modular architecture research tool; ODiNPred, prediction of order and disorder by evaluation of NMR data. Classification of NEMO based on the fraction of charged residues by CIDER: classification of intrinsically disordered ensemble regions. (B) Both N- and C-terminal domains are essential for phase separation of NEMO. Fusion proteins (5 µM) composed of MBP and WT NEMO-GFP, Q330X NEMO-GFP or CoZi-CTD NEMO-GFP (aa 249–419), or CoZi NEMO-GFP (aa 249–344) were incubated in presence of TEV protease to cleave off the MBP tag for 1 h at RT in buffer containing 10 mM Tris pH 7.4 ± 10 µM 4×M1-ub and then analyzed by fluorescent microscopy using a laser scanning microscope (scale bar, 10 µm).