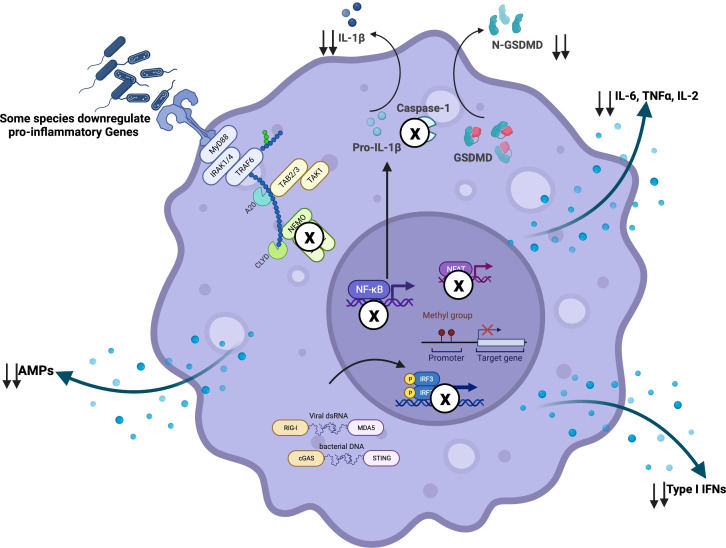
Figure 2.
Airway microbiome-driven immunomodulation: Airway microbiome downregulates pro-inflammatory signals via interference with immune signaling machinery. For instance, R. mucilaginosa has been shown to inhibit immune activation via NF-κB dependent mechanisms. As an immune evasion strategy, pathobionts have been described to inhibit TRIF and NFAT signaling, phagolysosomal fusion and acidification, as well as inflammasome activation. In other scenarios, gene methylation may promote transcriptional repression of pro-inflammatory genes. Created with BioRender.com.