-
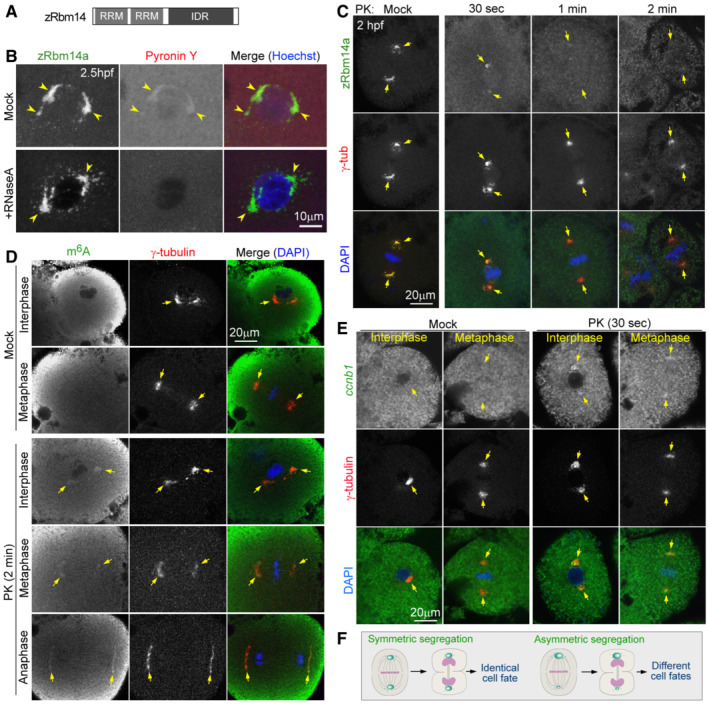
A
A diagram of zRbm14. RRM, RNA‐recognition motif; IDR, intrinsically‐disordered region.
-
B
zRbm14a condensates contained RNA. Zebrafish embryos fixed at 2.5 hpf were treated with RNase A or mock‐treated, followed by immunofluorescent staining to label endogenous Rbm14a and fluorescent staining with Pyronin Y and Hoechst 33342 to respectively label RNA and nuclear DNA. Maximum intensity‐projected confocal images are presented. Arrowheads point to representative condensates.
-
C
zRbm14a in condensates was sensitive to proteinase K (PK) digestion, whereas γ‐tubulin was resistant to the digestion. Maximum intensity‐projected confocal images are presented. Arrows point to spindle poles.
-
D, E
PK digestion exposed m6A‐modified maternal RNAs (D) and maternal ccnb1 mRNA (E) in zRbm14 condensates of both interphase and mitotic blastomeres in 2‐hpf embryos. As the high background fluorescent signals, probably due to high levels of dispersed RNAs in the cytoplasm, tended to obscure the spindle‐pole RNA signals in maximum intensity‐projected images, confocal images of a representative single optical section are shown.
-
F
Speculative illustrations for possible cell fate‐regulatory functions of zRbm14 condensates (green) by asymmetrically or symmetrically allocating maternal mRNAs in mitosis. The diagrams are not drawn to scale.