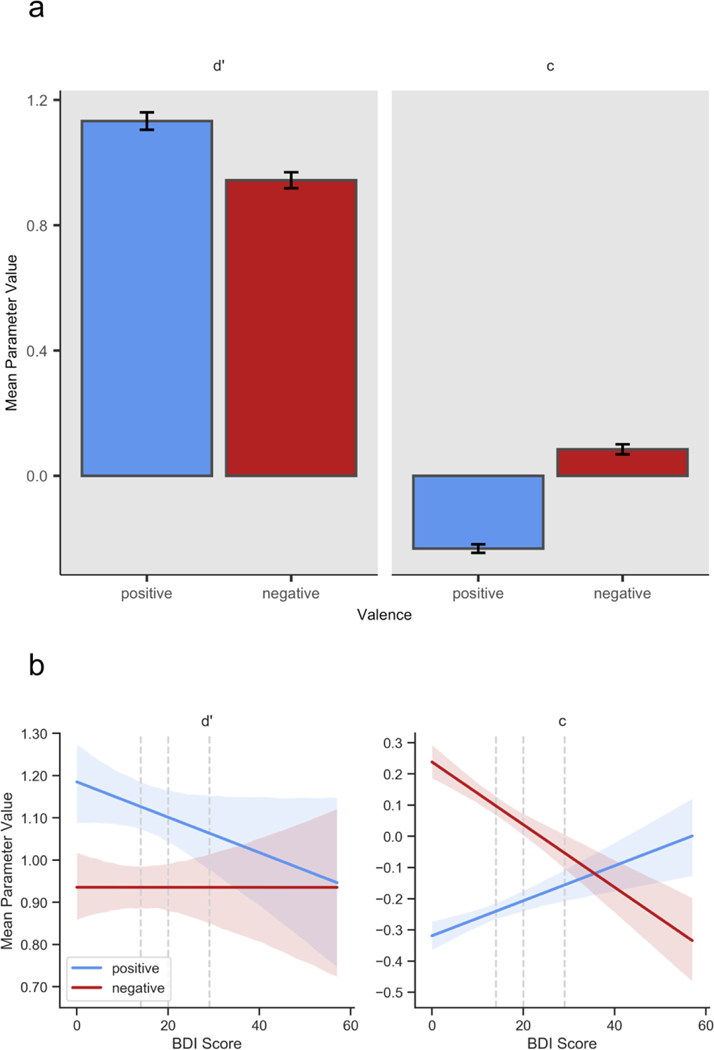
Figure 8.
SDT parameter values for source memory. In each panel, columns denote parameter (left: d’, right: c), and colors denote normative valence (blue: positive, red: negative). Error bars and bands represent 95% bootstrap confidence intervals (Waskom et al., 2017). In Panel (b), dashed vertical lines denote standard cutoffs for mild, moderate, and severe depression. Panel (a) depicts higher average values of d’ and lower (more liberal) average values of c for positive vs. negative words. Panel (b) demonstrates that as BDI score increases, d’ decreases slightly for positive words but is unaffected for negative words, and that c decreases (becomes more liberal) for negative words but increases (becomes more conservative) for positive words. In the context of this model, the results for c indicate that higher BDI scores are associated with a greater tendency to attribute old negative words to the self-referential encoding task and old positive words to the valence task.