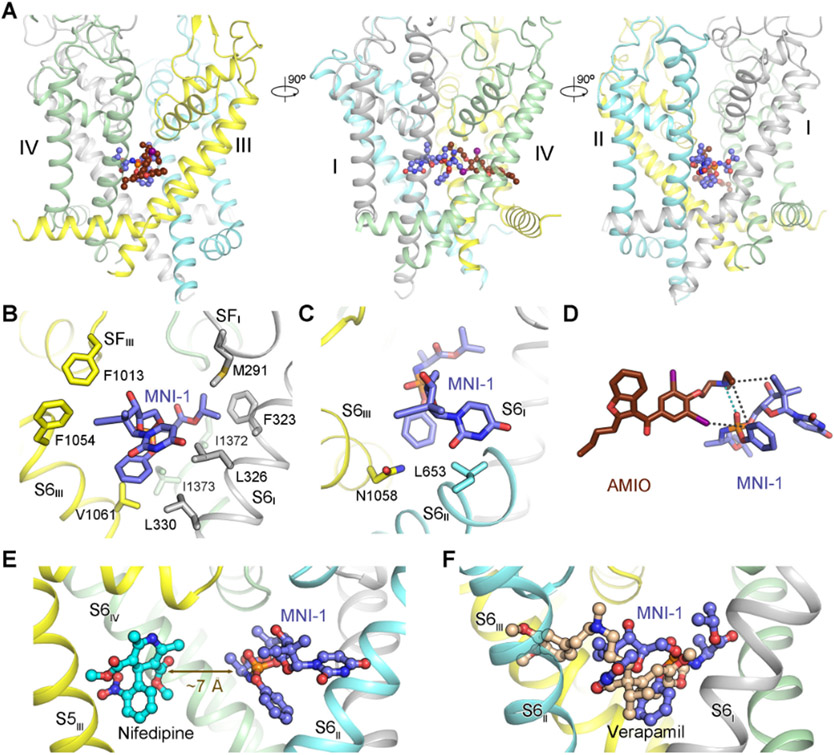
Figure 3 ∣. Direct drug-drug interaction (DDI) of AMIO and MNI-1 on rCav1.1.
(A) In the presence of AMIO, MNI-1 is accommodated in the central cavity of the PD. Three perpendicular side views of the PD are shown. AMIO and MNI-1 are shown as brown and purple ball-and-sticks, respectively. (B) The amphiphilic MNI-1 molecule is placed in a highly hydrophobic environment in rCav1.1. The MNI-1 coordinating residues, which are all hydrophobic, are shown as sticks. Repeat II and AMIO are omitted for visual clarity. (C) Less favored interactions between MNI-1 and rCav1.1 pore residues. Leu653 and Asn1058 are adjacent to polar and hydrophobic groups of MNI-1, respectively. (D) Direct interaction of AMIO and MNI-1. The polar interaction between the tertiary amine group in AMIO and the phosphate group in MNI-1 is indicated by cyan, dashed lines. The hydrophobic contacts between the two compounds are indicated by black, dashed lines. (E) Nifedipine does not interact with MNI-1 in rCav1.1. When the structure of nifedipine-bound rCav1.1 (PDB code: 6JP5) is overlaid with that of rCav1.1AM, the shortest distance between nifedipine and MNI-1 is ~ 7 Å, beyond the range for direction interactions. As the two structures are nearly identical, the protein scaffold of nifedipine-bound rCav1.1 is not shown. S6III and AMIO in rCav1.1AM are also omitted for clarity. (F) Overlapped binding poses of verapamil and MNI-1 explain their competition for binding to LTCCs. Verapamil-bound rCav1.1 structure (PDB code: 6JPA) is used for comparison with rCav1.1AM, but only the ligand is shown. See also Figure S3.