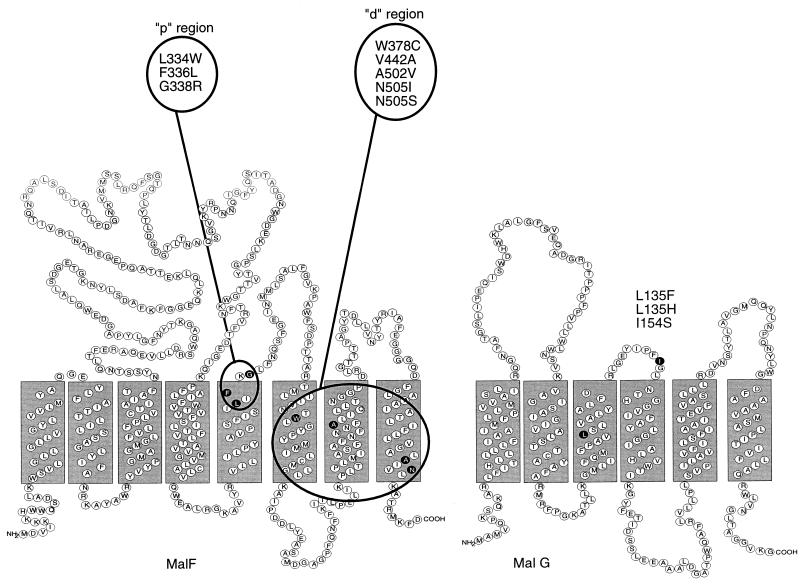
FIG. 4.
Two-dimensional structure of MalF and MalG. A topological model of MalF and MalG based on the analysis of malF::phoA and malG::phoA fusions is shown. MBP-independent mutants always require two mutations, one in the p (proximal) region and one in the d (distal) region. The G338R mutation in MalF alone causes MBP-dependent lactose transport. The EAAXXLG consensus motif is located in the cytoplasmic loop between MSS 6 and 7 of MalF and MSS 4 and 5 of MalG. Reprinted from reference 41 with permission of the publisher.