Fig. 1.
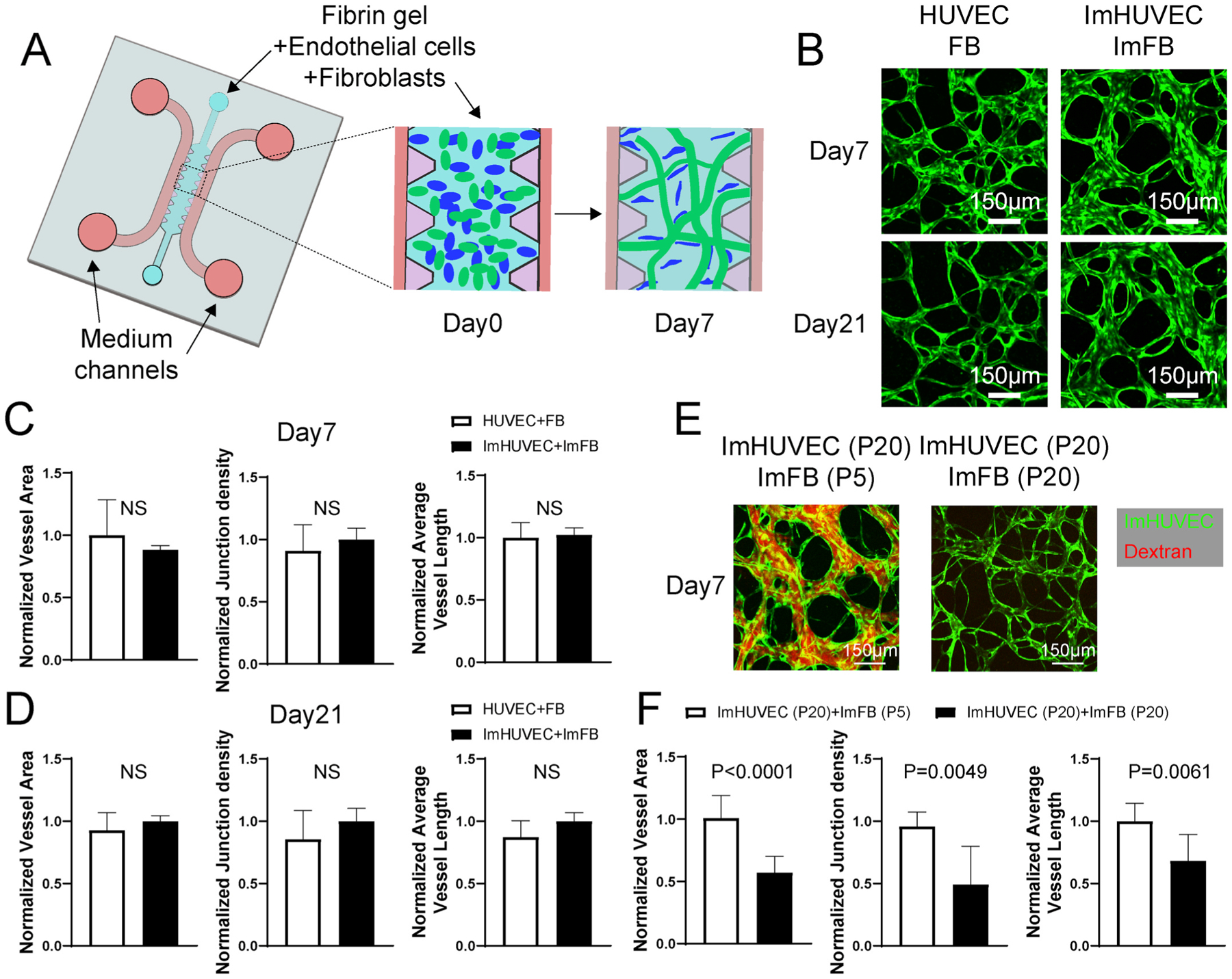
ImHUVECs form better μVNs with ImFBs from earlier passages than with ImFBs from later passages. (A) Schematic diagram of the AIMchip used to generate microvascular networks (μVNs) encapsulated in fibrin gel. Endothelial cells (ECs) and fibroblasts (FBs) mixtures are seeded on day 0 and form μVNs by day 7. (B) Representative images of μVNs made of parental HUVECs and FBs, as well as immortalized HUVECs (ImHUVECs) and immortalized FBs (ImFBs) on day 7 and day 21. Green: ECs. (C–D) Normalized vessel area (left), junction density (middle), and average vessel length (right) analyses of μVNs made of HUVECs with FBs or ImHUVECs with ImFBs on day 7 (C) and day 21 (D). (E) Representative images of μVNs made of ImHUVECs (green) from passage 20 (P20) with ImFBs from passage 5 (P5) or ImFBs from P20. μVNs are perfused with Texas Red dextran (red). (F) Normalized vessel area (left), junction density (middle), and average vessel length (right) analyses of μVNs made of ImHUVECs (P20) with ImFBs (P5) or ImFBs (P20). Bars represent mean ± SD. Two-tailed t tests were performed for the statistical comparisons. Scale bar is 150 μm.
