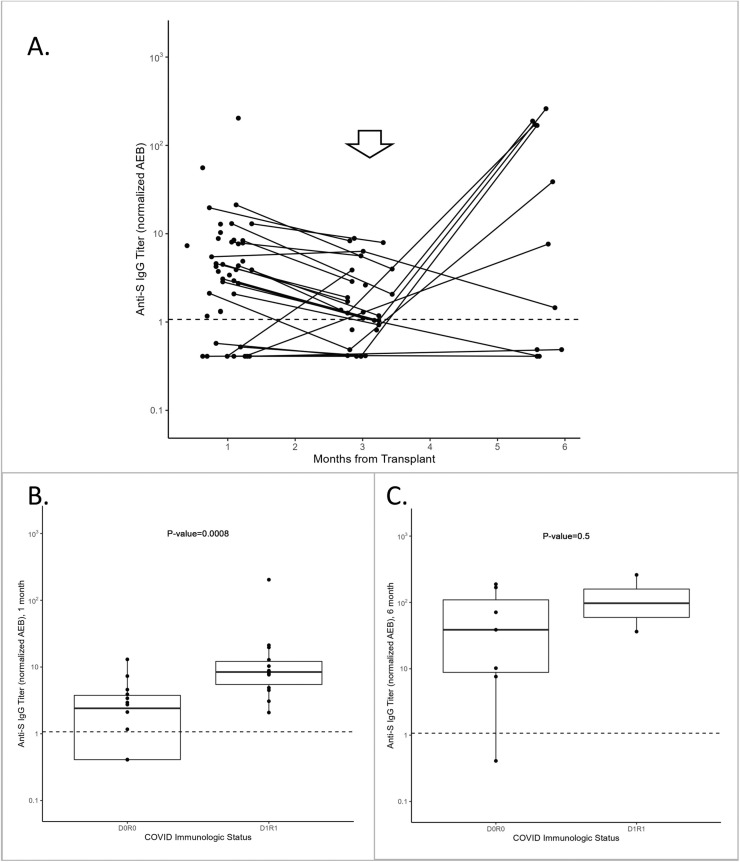
Figure 1.
(A) Anti-S IgG titers, in nAEB, in all recipients (n = 53) at 1, 3, and 6 months post-transplantation. The arrow indicates the approximate time of vaccination post-transplantation (∼3 months). (B) Anti-S IgG titers were analyzed at 1 month post-transplantation by immunologic status (D, donor; R, recipient; 0, no prior SARS-CoV-2 vaccination or infection before transplantation; 1, prior SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and/or infection before transplantation) for D0R0 (n = 14) and D1R1 (n = 14). The median titer was significantly higher for the D1R1 group compared with the D0R0 group (P = .008). (C) The anti-S IgG titers for recipients who were vaccinated between 3 and 6 months post-transplantation are represented by COVID-19 immunologic status, D0R0 (n = 7) or D1R1 (n = 2). Anti-S titers are shown at 6 months post-transplantation. No significant difference is observed between the D0R0 and D1R1 groups (P = .5). Values are median and IQR, and the dotted line at 1.07 nAEB represents the assay cutoff.