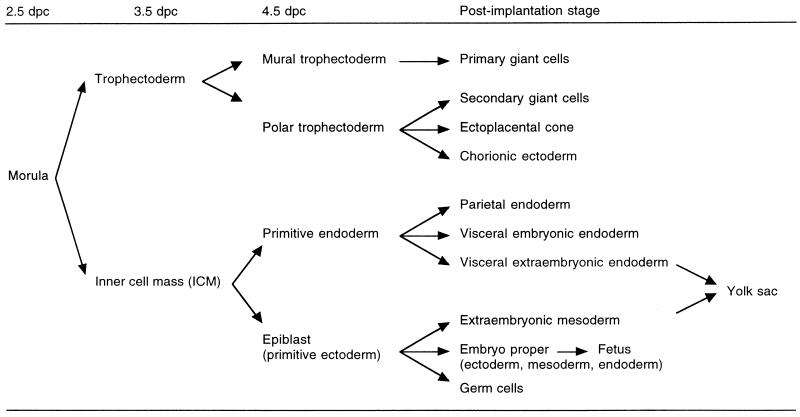
FIG. 2.
Diagrammatic representation of cell differentiation during mouse development. The trophectoderm is the first cell lineage, which differentiates at 3.5 dpc. Then the primitive endoderm differentiates, at 4.5 dpc. In the derivatives of these two extraembryonic cell lineages, XCI is nonrandom, in that the paternally inherited X chromosome is preferentially inactivated (see Table 1 for summary). In contrast, XCI is random in the epiblast, which gives rise to the yolk sac mesoderm, the embryo proper, and the primordial germ cells; i.e., either the paternal or the maternal X chromosome is inactivated in a given cell.