Figure 3.
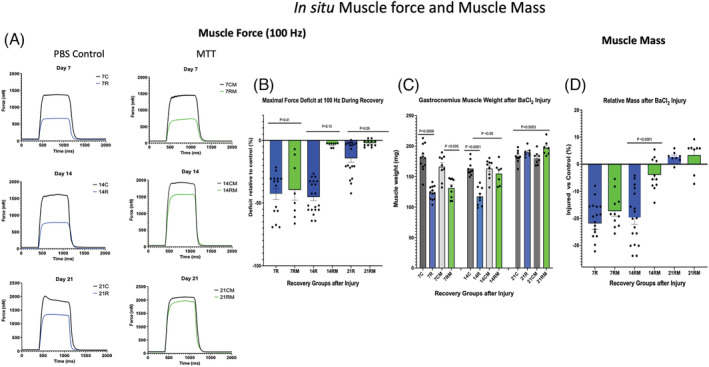
In situ muscle force and muscle mass. (A) Representative plantar flexor force records obtained at 100‐Hz frequency for phosphate‐buffered saline (PBS) sham‐treated mice and mitochondrial transplant therapy (MTT)‐treated mice 7, 14 or 21 days following BaCl2 injury of the gastrocnemius on one leg. Control muscles (C) were injected with PBS and not injured. Control force records are for 7 days (7C), 14 days (14C) or 21 days (21C) after injury of the intra‐animal control muscle. All BaCl2‐injured mice received a tail vein injection of PBS or MTT. PBS (sham‐treated) mice were examined after 7 days of repair (7R), 14 days of repair (14R) or 21 days of repair (21R) following injury. Mice that received donor mitochondria (MTT‐treated mice) were also examined after 7 days of mitochondria supplemented repair (7RM), 14 days of mitochondria repair (14RM) or 21 days of mitochondria repair (21RM) following injury. (B) the force deficit of the BaCl2‐injured muscle (expressed the percentage of the respective uninjured intra‐animal control muscle) was measured 7 days post‐injury in mice after systemic treatment with PBS (7R) or MTT (7RM). In other mice, the control and injured muscles were examined 14 days after injury in PBS‐treated (14R) or MTT‐treated (14RM), or after 21 days post‐injury in PBS‐treated (21R) or MTT‐treated (21RM) gastrocnemius muscles. P values are shown over the data. (C) Absolute muscle wet weight was obtained in control and injured gastrocnemius muscles. Mice were injected systemically with PBS (sham) or with mitochondria (MTT). Control uninjured muscles from PBS‐treated animals were obtained after 7 days (7C), 14 days (14C) or 21 days (21C) after injury of the opposite limb. Injured muscles of PBS‐treated animals were examined or after 7 days of repair (7R), 14 days of repair (14R) or 21 days of repair (21R) following injury. Other injured mice received systemically delivered donor mitochondria (MTT treated). Control uninjured (PBS‐injected) muscles from MTT‐treated animals were obtained after 7 days (7CM), 14 days (14CM) or 21 days (21CM) after injury of the opposite limb. The damaged‐repairing muscles were examined after 7 days of mitochondria‐supplement repair (7RM), 14 days of mitochondria repair (14RM) or 21 days of mitochondria repair (21RM) following injury. P values are shown over the data. (D) The relative gastrocnemius muscle mass of the injured muscle is presented as a percentage of the corresponding uninjured (PBS‐injected) intra‐animal control muscle after 7 days after injury in PBS (7R) or MTT (7RM) mice, 14 days after injury in PBS (14R) or MTT (14RM) mice, or 21 days after injury in PBS (21R) or MTT (21RM) mice. There was a significant difference between PBS‐treated and MTT‐treated muscle for the 14‐day group.
