Figure 5.
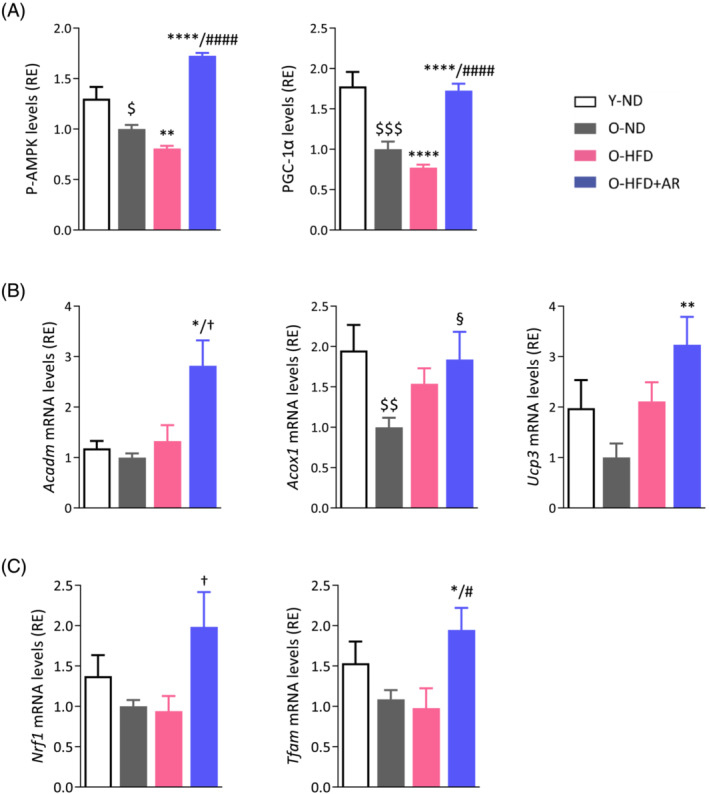
AdipoRon increases or tends to increase the expression of genes involved in fatty acid oxidation, mitochondrial biogenesis and function in soleus of middle‐aged obese mice. (A) AMPK activity and protein levels of PGC‐1α (gastrocnemius), early signalling events of the cascade leading to enhancing effects on mitochondria. (B) mRNA levels of medium‐chain acyl‐CoA dehydrogenase (Acadm) and acyl‐CoA oxidase 1 (Acox1) implicated in fatty acid oxidation and uncoupling protein 3 (Ucp3) in energy dissipation. (C) mRNA levels of nuclear respiratory factor‐1 (Nrf1), a target gene of PGC‐1α and of mitochondrial transcription factor A (Tfam). mRNA levels were normalized to cyclophilin, and the subsequent ratios presented as relative expression compared with O‐ND values. The active phosphorylated form of AMPKα (P‐AMPK) and PGC‐1α protein levels were quantified by ELISA, and absorbance data were presented as relative expression compared with O‐ND values. Data are means ± SEM for 6 Y‐ND, and 8–10 mice in the other three groups (A–C). Statistical analysis was performed by one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test (comparing three groups of O‐mice) or by unpaired two‐tailed t‐test (Y‐ND vs. O‐ND). $ P < 0.05, $$ P < 0.01, $$$ P < 0.001 versus Y‐ND mice. § P = 0.059, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 versus O‐ND mice. † P ≤ 0.08, # P < 0.05, #### P < 0.0001 versus O‐HFD mice.
