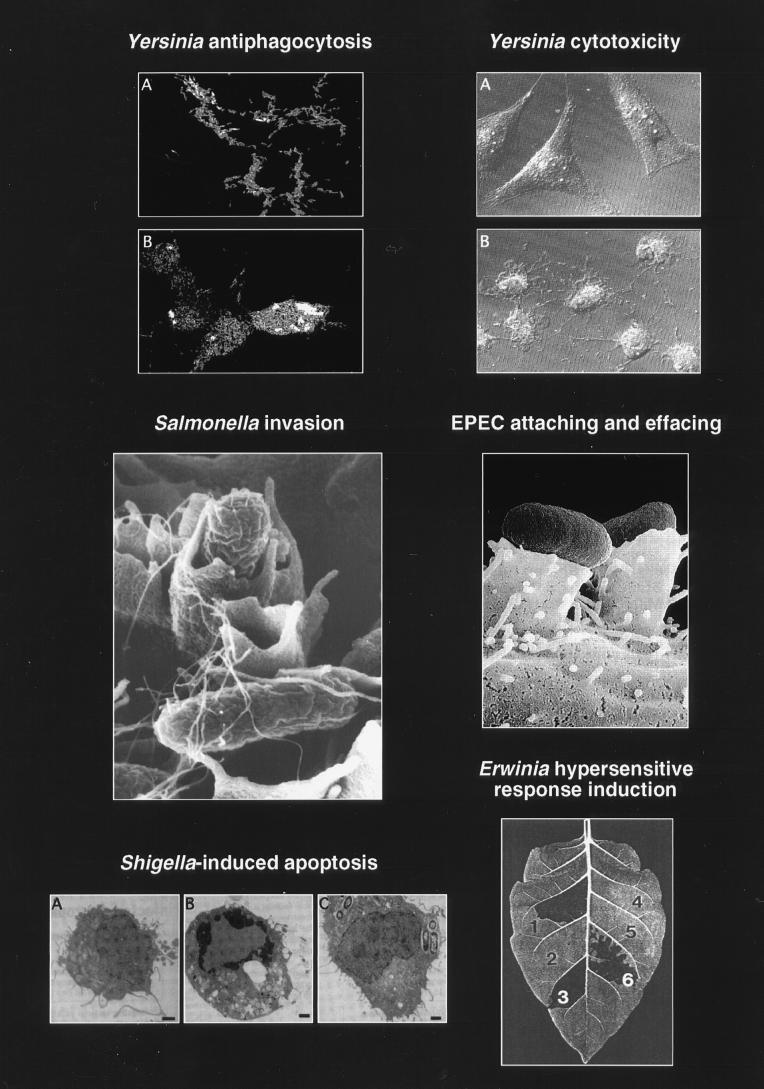
FIG. 2.
Selected phenotypic effects of type III secretion pathogenicity mechanisms on host cells and host tissue. (Top left) Panel B shows how Y. pseudotuberculosis injects (translocates) YopH (immunostained, light) into the cytosol of HeLa cells. Translocation of YopH into macrophages results in inhibition of phagocytosis. Panel A shows a type III secretion mutant: YopH is detected only in association with the bacteria. Reprinted with permission from reference 345. (Top right) Panel B shows the cytotoxic effect of Y. pseudotuberculosis on cultured HeLa cells. Translocation of YopE leads to a collapse of the cytoskeleton. Panel A shows uninfected HeLa cells. Reprinted with permission from reference 383. (Middle left) Invasion of a polarized HEp-2 epithelial cell via the induction of membrane ruffling by S. typhimurium. This figure has previously appeared on the cover of Mol. Microbiol. 1995, vol. 18 no. 3. Reprinted with permission. (Middle right) Pseudopod (pedestal) formation induced by EPEC on HeLa epithelial cells. Reprinted with permission from reference 378. (Bottom left) Induction of apoptosis in macrophages infected with S. flexneri. Panel A shows an uninfected macrophage. Panel B shows an apoptotic macrophage infected with wild-type S. flexneri. Panel C shows a macrophage infected with a S. flexneri type III secretion mutant. Reprinted with permission from reference 509. (Bottom right) Induction of localized tissue necrosis (HR) in a tobacco leaf at sites of infiltration with Erwinia spp. (area 1), buffer alone (area 4), type III secretion mutants (areas 2 and 5), and complemented mutants (areas 3 and 6). Reprinted with permission from reference 34.