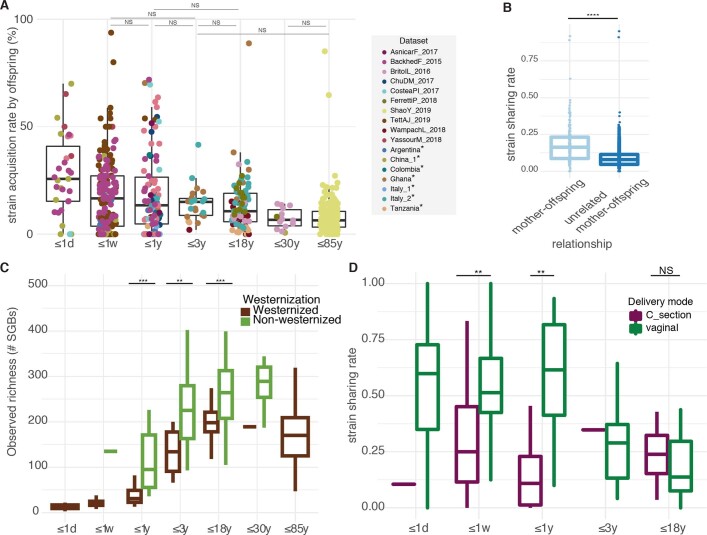
Extended Data Fig. 6. Mother to offspring gut microbiome transmission.
A) Strain acquisition rates by the offspring tend to decrease as a function of the offspring’s age. Strain acquisition rates by the offspring are defined as the proportion of strains profiled in the offspring that are shared with their mother, computed in 17 datasets from 14 different countries across pre-defined age categories. Kruskal-Wallis test, Chi2=65, P = 3.57e-12, Post-hoc Dunn tests, NS corresponds to Padj≥0.05, all other comparisons are significant (Table S10). Boxes: lower and upper quartiles, middle line: median; whiskers: 1.5 × IQR. Novel datasets are highlighted with asterisks. B) Strain sharing rates between senior individuals and their non-cohabiting mothers as compared to strain sharing rates between unrelated mother-offspring pairs. Wilcoxon rank-sum test, N = 17,177, r = 0.09, P = 4.1e-35. Boxes: lower and upper quartiles, middle line: median; whiskers: 1.5 × IQR. C) Observed richness (number of SGBs detected with MetaPhlAn) in age categories of offspring from Westernized as compared to non-Westernized populations. Wilcoxon rank-sum tests, N = 721, ***Padj <0.001 and **Padj<0.01, Table S11. Boxes: lower and upper quartiles, middle line: median; whiskers: 1.5 × IQR. D) Mother-offspring strain sharing rates in age categories of offspring delivered by C-section as compared to vaginally-delivered offspring. Wilcoxon rank-sum tests, **Padj<0.01, NS Padj≥0.05, Table S14. Boxes: lower and upper quartiles, middle line: median; whiskers: 1.5 × IQR.