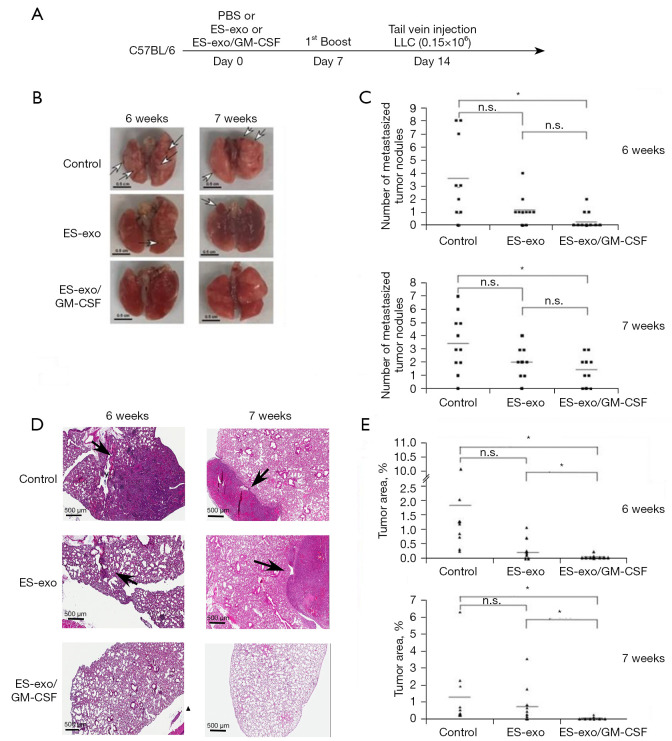
Figure 3.
ES-exo/GM-CSF vaccination inhibits the outgrowth of metastatic lung tumors. (A) The scheme of vaccination is depicted. Female C57BL/6 mice were immunized twice (Days 0 and 7) with vehicle control (PBS), ES-exo or ES-exo/GM-CSF prior to tail vein injection with LLC cells (0.15×106) on Day 14. Lung tumor development was examined at 6 weeks or at 7 weeks after LLC injection. (B) Representative images of lungs resected from euthanized mice. Surface tumor nodules were indicated by arrows. Scale bar, 0.5 cm. (C) Surface tumor nodules of resected lungs were enumerated by inspection. The data are presented as a dot graph of the number of surface tumor nodules of lungs. In the experiments carried out at 6 weeks after LLC injection, 10 mice in each group were evaluated. In the studies performed at 7 weeks following LLC challenge, n=11 mice in control group, n=9 mice in ES-exo group and n=10 mice in ES-exo/GM-CSF group were examined. *, P<0.05; ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (D) The histological sections of resected lungs were examined by H&E staining. Representative images of lung sections are shown (magnification: ×200). Lesions on lung sections are indicted by arrows. Scale bar, 500 µM. (E) The tumor lesion areas of each lung tissue sections were measured. The percentage of total lung area taken up by tumor tissues was quantified via measurements on H&E sections of resected lungs from animals in each group. For each lung, the average value of 3 sections with 50 microns apart was calculated. *, P<0.05; ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. PBS, phosphate buffered saline; ES, embryonic stem; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor; LLC, Lewis lung carcinoma; n.s. not significant; ANOVA, analysis of variance; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin.