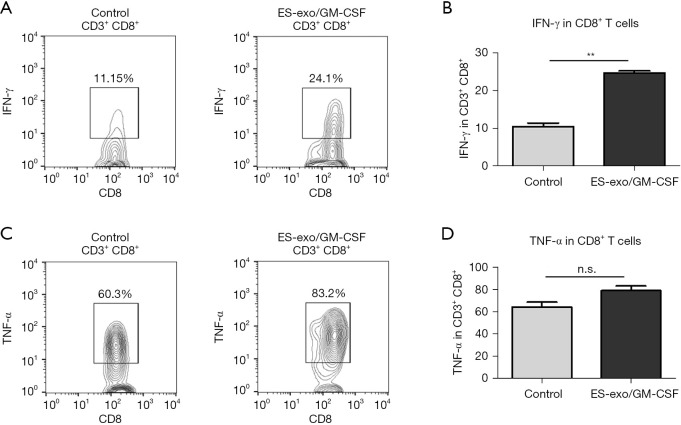
Figure 5.
ES-exo/GM-CSF vaccination promotes anti-tumor cytokine production. Female C57BL/6 mice were immunized twice (days 0 and 7) with vehicle control (PBS) or ES-exo/GM-CSF prior to tail vein injection with LLC. Five weeks after LLC challenge, lung tumors were resected, tumor-infiltrating cells were harvested and stimulated with LLC cell lysate for 6 hours. Intratumoral immune cells were identified by the pan-hematopoietic marker CD45 and intracellular expression of IFN-γ and TNF-α was examined by flow cytometry. (A) Dot plots showing IFN-γ expression in tumor-infiltrating CD3+CD8+ T cells obtained from control and ES-exo/GM-CSF-vaccinated mice. Numbers in plots represent the percentages of each subpopulation. (B) The data shown in (A) are summarized with 4 mice in control group, 6 mice in ES-exo/GM-CSF group. Mean ± SD, **, P<0.01; ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (C) The intracellular expression of TNF-α in tumor-infiltrating CD45+CD3+CD8+ cells was examined by flow cytometry. Numbers indicated in plots are the percentage of each subpopulation. (D) Bar graphs showing average of percentages of TNF-α+ in intratumoral CD3+CD8+ T cells from control and ES-exo/GM-CSF-vaccinated mice (n=4 in control group, n=6 in ES-exo/GM-CSF group); mean ± SD; ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. ES, embryonic stem; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor; n.s. not significant; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; LLC, Lewis lung carcinoma; SD, standard deviation; ANOVA, analysis of variance.