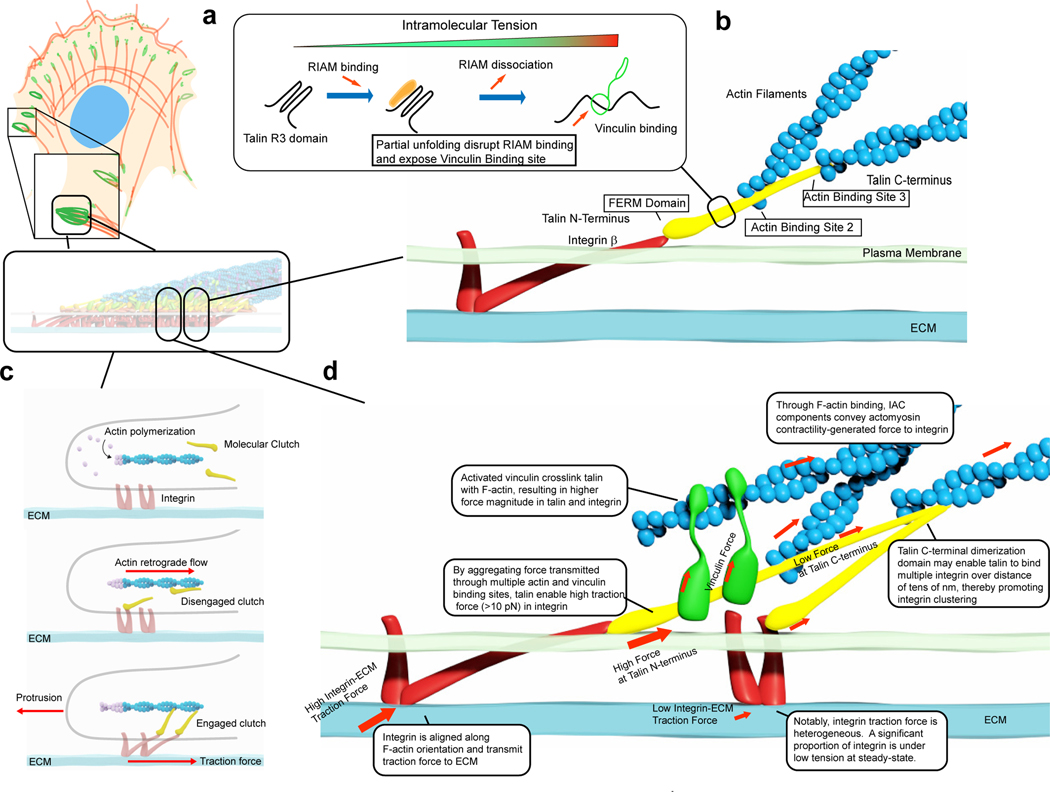
Figure 4 |. Molecular-scale mechanoregulation of IACs.
a | Mechanotransduction by force-dependent conformational changes. Several IAC proteins such as talin, vinculin, RIAM, α-actinin, KANK1 and filamin A contain domains that can be partially unfolded under piconewton physiological forces91,127–130. For example, talin R3 domain is a 4-bundle of α-helix that contains a binding site for RIAM. RIAM can bind talin under low intramolecular tension but upon the increase in intramolecular tension, R3 undergoes partial unfolding that displaces RIAM and in turn exposes a binding site to vinculin128. b | Integrin-Talin-Actin as the structural and mechanical ‘backbone’ of the IACs. In mature focal adhesions, talin adopt a vertically polarized orientation with N-terminal FERM domain engaging integrin b cytoplasmic tail. Actin binding sites 2 and 3 provide direct linkage to the F-actin cytoskeleton while indirect cross-linking is mediated by vinculin. c | Molecular clutch model of IAC mechanotransduction. Clutch molecules are capable of binding to both integrin and actin filaments. If molecular clutch is disengaged (middle panel), rearward force generated by actin polymerization in lamellipodia is primarily channeled to actin retrograde flow. Upon molecular clutch engagement (bottom panel), actin retrograde flow is mechanically coupled into traction force and support leading edge protrusion. d | Molecular-scale force transmission in IACs. Schematic diagram of force transmission in integrin-talinvinculin-actin complexes. Single-integrin force vector is primarily co-aligned with the F-actin orientation, potentially implicating a significant degree of tilting and stretching of the integrin ectodomain136,137. Integrin force is thought to be transmitted via talin, which may serve as a force aggregator as reflected by the intramolecular force gradient due to multiple vinculin and actin binding sites144,145. Load-bearing by integrin and talin are variable with high-load bearing molecules (>10 pN) comprising a subpopulation, dependent on vinculin139,145. Thus at steady-state only a subset of integrin-talin-vinculin-actin complexes in IACs are fully tensioned139.