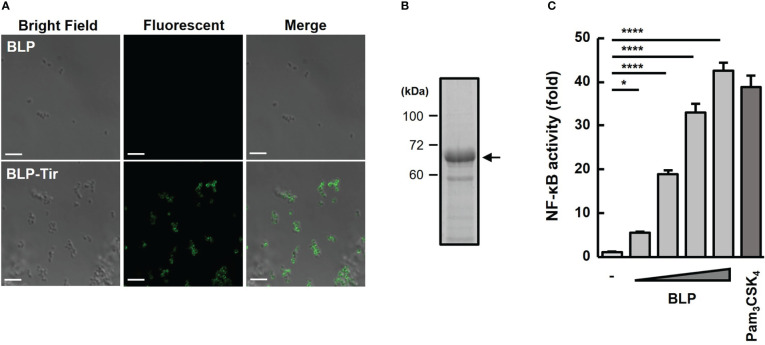
Figure 1.
Confirmation of Tir-LysM binding to BLPs. (A) Immunofluorescent microscopic images of BLPs alone (upper) and BLP-Tir (Tir-LysM-bound BLP, bottom) labeled with anti-Tir mouse serum and FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG. Bars, 5 μm. (B) BLP-Tir (2 × 109) was separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by CBB-staining. An arrow indicates 66 kDa BLP-Tir. (C) In vitro assessment of the TLR2 ligand activity of BLPs. Luciferase expression driven by NF-κB activation in HEK293T-TLR2 reporter cells was measured. Cells were stimulated for 24 h with PBS (-, negative control), BLPs (2, 8, 32 and 128 μg/ml), or Pam3CSK4 (100 ng/ml, synthetic TLR2 ligand, positive control). Data were expressed as the means ± SD (n = 3). *, p<0.05 and ****, p<0.0001; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.