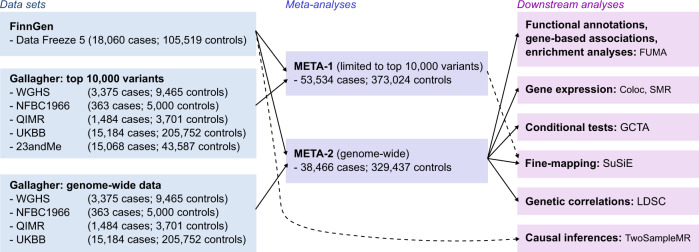
Fig. 1. Study setting.
The flow diagram illustrates the data usage and analytical steps of our study. We conducted a GWAS of uterine leiomyomata (UL) in 18,060 cases and 150,519 female controls from the FinnGen project. Subsequently, we meta-analysed the FinnGen-based results with summary statistics from a previous UL meta-GWAS12. META-1 included 53,534 cases and 373,024 female controls and was restricted to the top 10,000 variants from the previous study12. META-2 was conducted genome-widely in 38,466 cases and 329,437 female controls, excluding 23andMe data due to the data usage policy. Downstream analyses assessing functional annotations, gene-based associations, pathway enrichment, conditional association tests, fine-mapping, and genetic correlations were conducted using genome-wide summary statistics from META-2. In addition, fine-mapping was also conducted for the results of META-1. In Mendelian randomisation analyses evaluating causal inferences between UL and other, mostly UKBB-based traits, we extracted instruments for UL from the FinnGen-based summary statistics to avoid possible bias from overlapping UKBB samples.