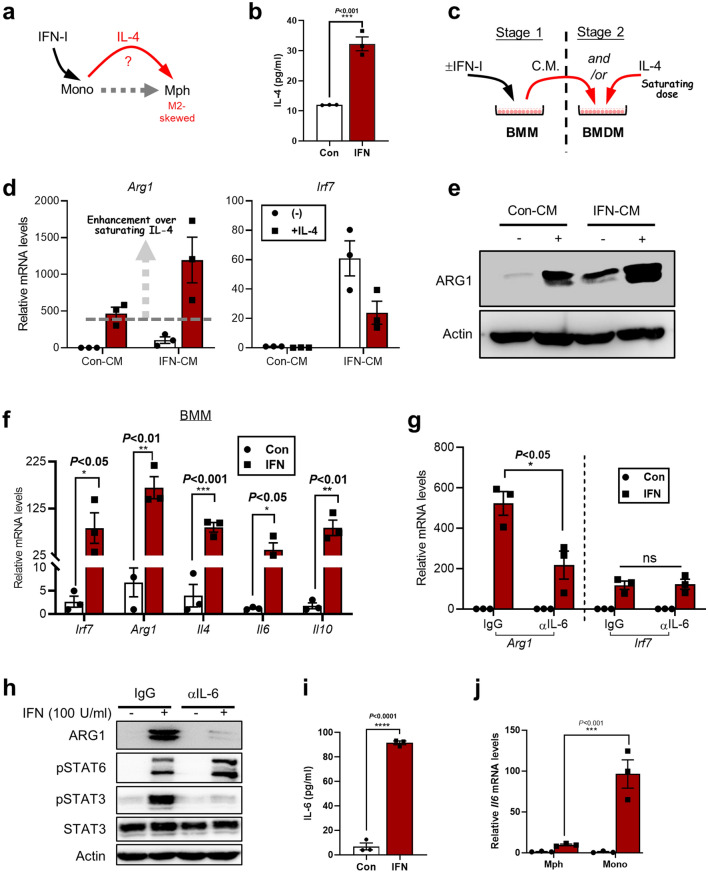
Figure 1.
IFN-stimulated transitional monocytes release IL-6 to promote IL-4-mediated induction of ARG1 in macrophages. (a) A schematic drawing shows the hypothesis that IFN-treatment of monocytes may release of a yet-to-be determined soluble factor(s) that acts together with previously established IL-4 to drive the M2-skewing of mature macrophages. The differentiation transition from monocytes to macrophages is also denoted by a dotted arrow. (b) BM mononuclear cells were treated with IFN (100 U/ml) for 24 h in the presence of M-CSF (20 ng/ml), the production of IL-4 in cell supernatants was determined by ELISA (n = 3, ± SEM). (c–e) The experiment scheme is shown in (c). In the first stage, BM mononuclear cells (BMM) were treated with M-SCF ± IFN for 48 h. The conditioned media (C.M.) were harvested. In the second stage, the C.M. from control or treated cells were transferred to naïve, mature macrophages (BMDMs). The BMDMs were treated for 48 h with either the C.M. alone or the C.M. and a saturating dose of IL-4. The cells were harvested and subjected to qPCR (n = 3, ± SEM) (d) or Western blot (WB) analyses (e). (f) BM mononuclear cells were treated with M-SCF ± IFN for 48 h, samples were harvested for mRNA analyses of indicated markers and cytokine genes (n = 3, ± SEM). (g,h) BM mononuclear cells were treated with M-CSF ± IFNβ for 48 h. In some groups, neutralizing Abs against IL-6 (5 μg/ml) were added to the medium as indicated. Samples were harvested after 48 h for mRNA [n = 3, ± SEM] (g) or protein (h) analyses. (i) BM mononuclear cells were treated with IFN for 24 h in the presence of M-CSF, the production of IL-6 in cell supernatants was determined by ELISA (n = 3, ± SEM). (j) BM mononuclear cells were treated with M-SCF ± IFN for 48 h, monocytes (Ly6C+F4/80−) and macrophages (F4/80+) were sorted by flow cytometry. Samples from sorted cells were subjected to qPCR analysis (n = 3, ± SEM). For most statistical analyses related to this figure, unpaired t tests were performed (P value marked on the graph). For (j), 2-way ANOVA tests were performed (the adjusted P value presented). Asterisks correspond to P values (****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05; ns not significant).