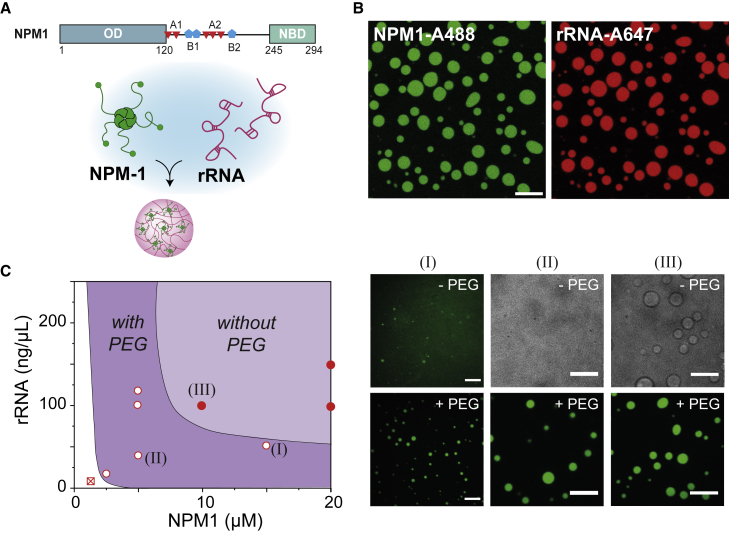
Figure 1.
PEG-induced phase separation of NPM1-rRNA. (A) Schematic illustration of nucleophosmin (NPM1) protein domains and the formation of condensates with rRNA. NPM1 encodes for a structural N-terminal oligomerization domain (OD) and a C-terminal nuclear binding domain (NBD) linked by an intrinsically disordered region with two acidic tracts (A1 and A2) and two weak basic tracts (B2 and B2). Pentamers of NPM1 phase separate with rRNA into condensates in vitro. (B) Fluorescent microscopy images of NPM1-rRNA condensates at 10 μM NPM1-Alexa488; 150 ng μL−1 rRNA-Alexa647 (in 10 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl). Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Schematic representation of the shift in phase boundary of NPM1-rRNA liquid-liquid phase separation as determined by preparing mixtures with different overall composition (51). Note that the drawn lines indicating the phase boundaries without PEG and with 2 wt % PEG are drawn to guide the eye and do not represent accurate binodal lines, in particular at rRNA concentrations above 125 ng μL−1. Three conditions have been highlighted with roman numerals, and microscopic images in the presence or absence of 2 wt % PEG are shown to the right: (I) 15 μM NPM1, 50 ng μL−1 (147 μM nt) rRNA, (II) 5 μM NPM1, 37.5 ng μL−1 (110 μM nt) rRNA, (III) 10 μM NPM1, 75 ng μL−1 (220 μM nt) rRNA. Scale bars, 10 μm.