FIGURE 4.
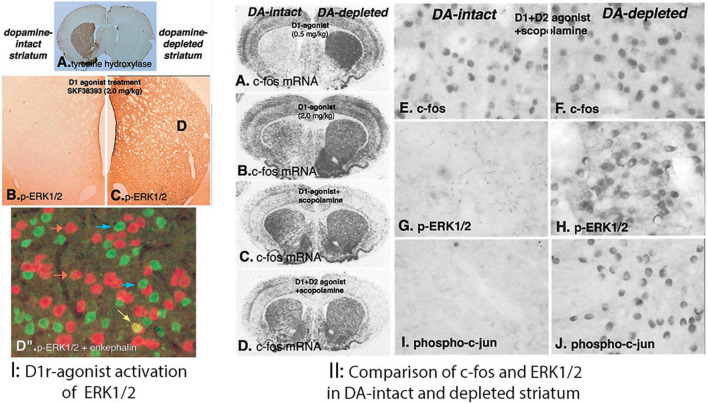
(I) D1 dopamine receptor-mediated phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2) in the dopamine-depleted striatum. Unilateral lesion of the nigrostriatal dopamine systems is demonstrated by the loss of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity in the right lesioned striatum (A). After treatment (15 min) with the partial D1 dopamine agonist SKF38393 (2 mg/kg, i.p.), p-ERK1/2 is not evident in the dopamine-intact striatum (B) but is present in numerous neurons in the dopamine-depleted striatum (C). To determine the type of striatal neuron in which p-ERK1/2 is present, sections were processed to display both p-ERK1/2 with a green fluorescent label and enkephalin mRNA with a red fluorescent label (D”). Nearly all p-ERK1/2-immunoreactive neurons (blue arrows) are enkephalin negative. Only a small number enkephalin-positive neurons display p-ERK1/2 immunoreactivity (yellow arrow), whereas the vast majority are p-ERK1/2 negative (orange arrows). (II) Demonstration of distinct mechanisms of D1 dopamine receptor-mediated gene regulation in the dopamine (DA)-intact and -depleted striatum, using the full D1 agonist SKF81297 alone or combined with other drugs. (A–D) In situ hybridization histochemical localization of mRNA encoding c-fos 45 min after different drug combinations: (A) SKF81297 (0.5 mg/kg); (B) SKF81297 (2.0 mg/kg); (C) SKF81297 (2.0 mg/kg) combined with the muscarinic receptor antagonist scopolamine (5 mg/kg); or (D) SKF81297 (2.0 mg/kg) combined with the D2 dopamine receptor agonist (1 mg/kg) and scopolamine. The low dose of agonist alone (A) demonstrates the supersensitive response by the selective induction of c-fos in the dopamine depleted striatum. Bilateral induction of c-fos IEG in both the dopamine-intact and -depleted striatum follows treatment with high dose of the full D1 agonist alone (B) or in combination with other drugs (C,D). However, when animals receiving any of these treatments (15 min survival) p-ERK1/2-immunoreactive neurons are evident only in the dopamine-depleted striatum and not in the dopamine-intact striatum (data not shown). The treatment combining full D1 agonist with both the D2 agonist and scopolamine produces the most robust c-fos IEG response in both the DA-intact (E) and DA-depleted (F) striatum at 45 min. This treatment also results in persistent p-ERK1/2 (H) and phosphorylated c-jun (J) in the dopamine-depleted striatum but does not activate p-ERK1/2 (G) or phosphorylated c-jun (I) in neurons in the dopamine-intact striatum. These results demonstrate that, although D1 dopamine receptor-mediated induction of the IEG c-fos occurs in both the dopamine intact and -depleted striatum, activation of ERK1/2 occurs only in the dopamine-depleted striatum (Gerfen et al., 2002).