Abstract
Colchicine has been demonstrated to reduce cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction (MI), ischemic stroke, and ischemia-driven coronary revascularization in people with coronary artery disease (CAD). These reductions were observed even in patients already taking antiplatelet therapy. As well as having anti-inflammatory effects, colchicine demonstrates antiplatelet effects. We propose that colchicine's antiplatelet effects primarily target collagen-induced platelet activation via the collagen receptor, glycoprotein (GP)VI, which is critical for arterial thrombosis formation. In settings such as stroke and MI, GPVI signaling is upregulated. We have demonstrated in vitro that therapeutic concentrations of colchicine lead to a decrease in collagen-induced platelet aggregation and alter GPVI signaling. Clinical studies of colchicine given for 6 months lead to a significant reduction in serum GPVI levels in CAD patients, which may ameliorate thrombotic risk. Future evaluation of the effects of colchicine in clinical trials should include assessment of its effects on collagen-mediated platelet activation, and consideration be given to quantifying the contribution of such antiplatelet effects additional to the known anti-inflammatory effects of colchicine.
Keywords: colchicine, platelet activation, GPVI, cardiovascular disease (CVD), stroke
Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD), including coronary artery disease (CAD) and cerebrovascular disease, remain the main cause of death in the world (1). The contribution of platelets to CVD initiation and progression is well evidenced and has now extended beyond thrombosis alone to include a role in inflammation [reviewed in Gawaz et al. (2), Nording et al. (3), and Rondina et al. (4)]. Platelets respond to both sub-endothelial collagen (upon endothelial dysfunction/disruption) via the collagen receptors [integrin α2β1 and glycoprotein (GP)VI], and to thrombin (generated at the site by activation of the coagulation system) via the protease-activated receptors (PAR)-1 and -4. The platelet activation response occurs rapidly and includes shape change, release of granular contents from both alpha- and dense-granules, and conformational change of receptors such as GPIIb/IIIa which allows for platelet aggregation. The dense granule release leads to secretion of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) which is involved in the secondary wave of platelet activation which enhances the platelet activation response.
Antiplatelet therapy in CVD [reviewed in Behan and Storey (5) and Passacquale et al. (6)] began with inhibition of the cyclo-oxygenase (COX)-1 pathway by aspirin, followed by inhibition of the ADP receptor, P2Y12, as an alternative or adjunct therapy to aspirin, and GPIIb/IIIa inhibition in acute coronary syndromes. In all cases, more potent or extensive antiplatelet inhibition has been associated with increased risk of bleeding. Completed (7, 8) and ongoing trials include alternative antiplatelet targets, including a collagen receptor (GPVI) (9, 10), and the thrombin receptors (PAR-1 and−4) [reviewed in Abdulsattar et al. (11) and Li et al. (12)]. Anti-inflammatory targets, including interleukin (IL)-1β and nucleotide-binding domain leucine rich-repeat containing protein (NLRP3) (13–18) have also been recently explored. Recent studies have identified that colchicine may work as both an anti-inflammatory [reviewed in Martinez et al. (19)] and antiplatelet agent (20, 21).
In this perspective, we aim to highlight the need to evaluate collagen-mediated platelet activation in clinical environments and in cardiovascular trials. This may clarify the potential role of this under-investigated activation pathway in mediating the effects of colchicine as an adjunctive CVD therapeutic agent.
Platelet function studies and CAD clinical trials
COX-1 and P2Y12 inhibition have been the cornerstones of antiplatelet therapy for cardiovascular disease for several decades (6, 22, 23). While dual antiplatelet therapy (e.g., aspirin and clopidogrel) has proven to be effective in reducing cardiovascular events in unstable angina pectoris patients and post PCI (24, 25), this treatment has some limitations such as residual high on-treatment platelet reactivity to ADP (26) and the bleeding complications caused by more potent P2Y12 inhibitors (27). Importantly, trials adjusting therapy based on testing platelet function using the level of P2Y12 inhibition were not effective in improving cardiovascular outcomes (28–30), suggesting limitations to our conventional approaches of assessing platelet function in patients with CVD. P2Y12 inhibition can have additional unexpected effects on platelet reactivity to both collagen and thrombin which are not explored during conventional platelet testing (31). While conventional platelet function testing is not currently recommended in patients undergoing PCI (32), there has been some success in ACS with de-escalation based on platelet function testing (33).
Despite the availability of diverse platelet function assays (34), clinical trials have focused on assays such as aggregometry, and ADP-dependent point of care assays (VerifyNow and TEG) and vasodilator-stimulated phospho-protein (VASP) phosphorylation [reviewed in Fontana et al. (35)]. Aggregation assays are dependent on both the agonists and the concentrations used, such as stimulating the P2Y12 receptor (29, 33). Additionally, results can differ according to sample type. Light transmission aggregometry (LTA) requires the use of platelet rich plasma (PRP), whereas impedance aggregometry allows for the use of either PRP or whole blood, and the latter may permit leukocyte contributions to platelet activation which may be more physiological. VASP phosphorylation, while informative for activity/signaling or response of the P2Y12 receptor to stimulation by ADP and thus the secondary augmentation response, does not inform in relation to other pathways of platelet activation. Despite platelets being anucleate and relatively small, their signaling and activation pathways are both complex and interconnected. The concept of individualized therapy is receiving more attention (29, 33), and rather than only looking at drug responsiveness with one assay/agonist, e.g., ADP, inclusion of other agonists such as collagen and thrombin may be informative.
Collagen-mediated platelet activation and the GPVI receptor
Platelet activation through the collagen receptors (integrin α2β1 and GPVI) is critical for the formation of arterial thrombosis and can lead to blockage of vessels resulting in myocardial infarction (MI) or stroke. Whereas, inhibiting more traditional targets such as GPIIb/IIIa (aka integrin αIIbβ3), P2Y12, and thromboxane A2 can lead to bleeding complications, it is possible that novel receptor targets such as the collegen receptor will not cause bleeding (9, 10, 36).
GPVI is solely expressed on platelets, as a mixture of monomers and dimers (37). It is the primary receptor for collagen, and collagen-mediated platelet activation via GPVI is dependent on receptor density (38). Binding between collagen and GPVI enhances activation of integrins such as α2β1 which increases adhesiveness of the platelets (39, 40). In the absence of GPVI, α2β1 is required for collagen-mediated platelet activation (40) but under physiological conditions GPVI is the main collagen receptor. Interestingly, collagen stimulation (at low concentrations) via GPVI can lead to secretion of platelet granule contents without causing other overt activation (expression of P-selectin (CD62P) or GPIIb/IIIa conformational change), aggregation or shape change (41). Thus, strategies leading to partial inhibition of GPVI signaling are attractive in CVD due to the ability to target pathological granule secretion while leaving the major haemostatic pathways intact.
Surface levels of GPVI expression are increased in acute coronary syndromes (ACS) independent of traditional markers of MI [e.g., creatine kinase (CK) and troponin T] (42). Moreover, patients who had increased GPVI levels also had increased platelet aggregability post coronary stenting despite dual antiplatelet therapy (42). GPVI expression levels could also be a potential marker of MI risk prior to the event (42–44). Additionally, ACS patients have an elevated number of GPVI receptors on circulating platelets before (Day 0) and after stenting (Day 1) when compared to patients with stable angina pectoris (SAP) which lasts up to 2–4 days post-PCI, and patients with an elevated level of GPVI at admission tended to have a poorer clinical prognosis (42). Enhanced collagen-induced aggregation in the presence of COX-1 inhibition (aspirin) can be indicative of future ACS events in otherwise healthy individuals who have a known family risk of early-onset CAD–only those individuals whose collagen-induced aggregation remained elevated after 2 weeks of aspirin, tested in whole blood, had an ACS event during follow-up, further underscoring the potential importance of collagen-mediated platelet activation in ACS (45).
During platelet activation, in response to both soluble platelet agonists and shear, GPVI forms dimers that preferentially bind to fibrous collagen when compared to the GPVI-monomer (46, 47). Inhibition of the binding between the GPVI-dimer and immobilized collagen leads to decreased platelet adhesion and aggregation (48). GPVI-dimer expression levels, but not total GPVI levels, have also been demonstrated to be elevated in stroke, with elevation being noted for ≥90 days post-stroke (49). This increase was associated with increased platelet activation and with stroke severity. Cleavage of GPVI by metalloproteinases is a feature of collagen-mediated platelet activation (50). This generates soluble GPVI (sGPVI), and increased levels of sGPVI have been demonstrated in stroke (51).
Revacept, a GPVI-Fc fusion protein, has shown some promise in reducing cerebral infarct volume and improving functional outcomes in a stroke model without bleeding complications (36). Revacept in combination with guideline recommended antiplatelet therapy has now undergone phase II clinical trials in symptomatic carotid stenosis. The clinical trial (n = 158 patients randomized to three groups; placebo, 40 and 120 mg Revacept) assessed the safety and efficacy of the treatment with the following end points—any cerebrovascular events (including stroke or MI) or bleeding complications. A 54% risk reduction in the safety and efficacy end points was observed in the highest dose (120 mg Revacept) group, demonstrating the potential of GPVI as a therapeutic target and a clear indication of the importance of collagen-mediated platelet activation (9).
Colchicine inhibits collagen mediated platelet activation
While it is well-known that colchicine affects the typical inflammatory cells such as monocytes and neutrophils, it is becoming increasingly evident that colchicine also influences platelets. We have recently reviewed the effect of colchicine on platelet function in both in vitro and in vivo settings (52).
Studies examining platelet aggregation in response to in vitro colchicine show that whereas inhibition of aggregation to several common platelet agonists requires micromolar concentrations of colchicine, nanomolar concentrations inhibit certain responses to thrombin (53, 54) and calcium ionophore (55). In our studies (20), platelet aggregation in whole blood and in platelet rich plasma in response to collagen (but not ADP) were inhibited by nanomolar concentrations of colchicine indicating that colchicine may be a novel method of biased targeting of GPVI.
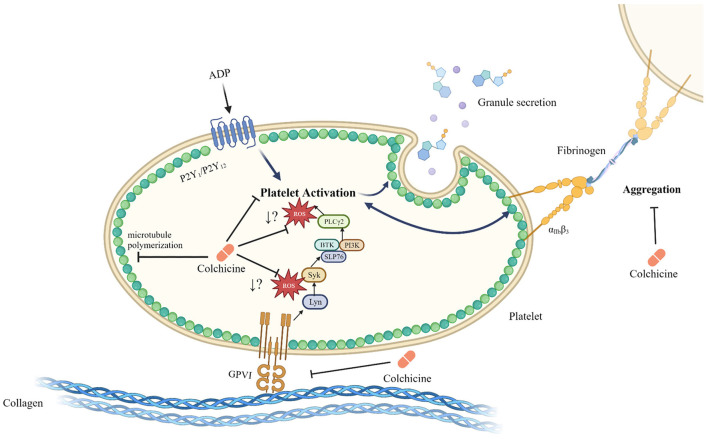
In our studies, stimulation of GPVI with CRP-XL (cross-linked collagen related peptide, specific for GPVI stimulation) generated reactive oxygen species (ROS), and colchicine led to a reduction in ROS generation in vitro (20) (Figure 1). Colchicine did not cause a reduction in GPVI surface expression, indicating that the observed effect was not due to a change in GPVI receptor number but rather a change in the signaling events downstream of the receptor binding. Colchicine decreased CRP-XL-stimulated P-selectin expression and trended toward a decrease in GPIIb/IIIa conformational change. A previous study also reported on the inhibitory effects of colchicine on collagen-mediated serotonin release from platelets (59).
Figure 1.
Schematic of the inhibitory role of colchicine in platelet activation. Colchicine modulates microtubule polymerization, but also leads to a reduction in platelet activation and aggregation. Colchicine does not change GPVI surface expression levels but does result in reduced ROS generation by platelets in response to stimulation of the GPVI receptor by CRP-XL; however, it is not known at what point within the GPVI signaling pathway ROS generation is affected. While the reduction in ROS generation in response to colchicine is specific to the GPVI signaling pathway, reduced activation by colchicine, particularly after stimulation with other agonists such as ADP, may be a microtubule depolymerization dependent effect. Whether colchicine directly interacts with the platelet GPVI receptor or acts exclusively downstream of this receptor is unknown. Created with Biorender.com (20, 52, 56–58).
In our in vitro studies, colchicine also led to a reduction in procoagulant platelet formation in response to thrombin-collagen dual stimulation (20), and this reduction in procoagulant platelet formation could be particularly important in the setting of MI and stroke. In a sub-study of the LoDoCo2 trial, a reduction in platelet/hemostasis related markers [GPVI, proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src (SRC) and CD40L] was noted (21) in response to colchicine lending plausibility to an in vivo antiplatelet effect. Given the already recognized anti-inflammatory effects of colchicine (14–18), colchicine may be more beneficial than targeting the GPVI receptor alone since it reduces both inflammatory and thrombotic responses.
Targeting the collagen receptor may be particularly relevant to at risk populations such as the elderly due to their risk of developing bleeding complications with other therapies (60). Platelets from elderly people have been shown to be hyperreactive to low dose collagen in terms of aggregation and ATP release (61). Colchicine inhibition of collagen-mediated platelet activation may therefore be particularly important in this population, especially as colchicine is not associated with increased rates of bleeding in recent cardiovascular trials. The use of colchicine in the elderly will, however, require particular care because of reduced renal function, increased susceptibility to the adverse effects of polypharmacy, and the risk of drug interactions.
Discussion
We have outlined the importance of 1) including a broader approach to platelet function studies during clinical trials; 2) the contribution of collagen-mediated platelet activation in diseases/conditions such as CAD, MI and stroke; and 3) the potential role of colchicine in targeting collagen receptor pathways.
As current antiplatelet therapy inhibits hemostasis and can lead to bleeding complications, colchicine may represent a useful adjunctive therapy to traditional antiplatelet therapies that does not appear to increase the risk of bleeding, and may be of particular benefit in clopidogrel non-responders (62). To fully understand the mechanistic processes underlying the protective effects of any medication, and colchicine in particular, against CVD, there is a pressing need for future clinical trials to specifically evaluate collagen-mediated platelet activation. This should be done in two ways. Firstly, and most simply, studies should measure soluble GPVI which is an indicator of prior platelet receptor activation in vivo. Secondly, and more laboriously, platelets from patients should be stimulated ex vivo using collagen (or CRP-XL) to indicate the residual responsiveness of platelets to collagen. This complementary information would allow the analysis of the effect of different agents—P2Y12 inhibitors, antithrombins, colchicine and newer agents—on specific platelet activation pathways via collagen that might be more revealing than conventional agonist assays simply stimulating using ADP.
Our understanding of the effectiveness of current antiplatelet regimes would also be enhanced by broadening the usual evaluation of residual platelet activity to include other agonists. Because P2Y12 receptor inhibitors inhibit the secondary augmentation response, they affect more pathways than just the P2Y12 receptor pathway, and the inclusion of other platelet activity tests and agonists such as thrombin and collagen receptor related pathways would clarify how much residual non P2Y12 receptor-mediated platelet activation is evident in different clinical or therapeutic scenarios. For example, in ACS patients receiving both aspirin and clopidogrel, a loading dose of clopidogrel reduced platelet aggregation, platelet activation, and platelet-leukocyte aggregates in response to both ADP receptor and PAR-1 stimulation (63). In vitro inhibition with cangrelor (an intravenous reversible P2Y12 inhibitor) led not only to a decrease in platelet responsiveness to ADP, but also to PAR-1 and PAR-4 (thrombin receptors) agonists and CRP-XL. This diminished response was also observed in relation to the release of dense granule contents (ATP and ADP) after stimulation with PAR-1 agonist and CRP-XL (31). In addition, in this study, the VerifyNow results did not agree with the GPIIb/IIIa binding results that were established by flow cytometric analysis, and this was attributed to the restriction of the VerifyNow assay to the P2Y12 pathway.
Recent clinical trials targeting GPVI either directly with ACT017, Voors-Pette et al. (10) or indirectly with Revacept, Uphaus et al. (9) have shown great promise in reducing collagen-mediated platelet activation and improved stroke outcome without leading to bleeding complications (64). Colchicine reduces the risk of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke (65–67), which is consistent with the reduction observed for Revacept both in a mouse stroke model (36) and a human carotid stenosis clinical trial (9), however colchicine has additional anti-inflammatory affects. Like ACT017 and Revacept, colchicine treatment has not been linked to bleeding complications. Other potential GPVI related targets, undergoing clinical trials and scientific investigation, have shown decreased platelet responses including aggregation, P-selectin expression and GPIIb/IIIa conformational change in response to multiple agonists, some of these targets are in use for treatment of hematological malignancies (68–70).
Although dual antiplatelet therapy has been effective in reducing cardiovascular events this has been at the risk of bleeding complications, particularly in the elderly. Colchicine and other emerging therapies may modulate platelet function in ways undetected by conventional platelet function assays. Diversifying our approach to platelet activation in vivo, and considering the effect of agents such as colchicine on platelets and not only inflammatory pathways may reveal new clinical opportunities for patient care without the associated bleeding risk.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
GP, LK, and CR wrote the first draft of the manuscript. GP, LK, CR, SG, and VC reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- 1.Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs): World Health Organization (2021) . Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed November 16, 2022).
- 2.Gawaz M, Langer H, May AE. Platelets in inflammation and atherogenesis. J Clin Invest. (2005) 115:3378–84. 10.1172/JCI27196 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nording HM, Seizer P, Langer HF. Platelets in inflammation and atherogenesis. Front Immunol. (2015) 6:98. 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00098 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rondina MT, Weyrich AS, Zimmerman GA. Platelets as cellular effectors of inflammation in vascular diseases. Circ Res. (2013) 112:1506–19. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.300512 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Behan MW, Storey RF. Antiplatelet therapy in cardiovascular disease. Postgraduate Med J. (2004) 80:155–64. 10.1136/pgmj.2003.007062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Passacquale G, Sharma P, Perera D, Ferro A. Antiplatelet therapy in cardiovascular disease: current status and future directions. Br J Clin Pharmacol. (2022) 88:2686–99. 10.1111/bcp.15221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bohula EA, Aylward PE, Bonaca MP, Corbalan RL, Kiss RG, Murphy SA, et al. Efficacy and safety of vorapaxar with and without a thienopyridine for secondary prevention in patients with previous myocardial infarction and no history of stroke or transient ischemic attack: results from TRA 2 degrees P-TIMI 50. Circulation. (2015) 132:1871–9. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.015042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tricoci P, Huang Z, Held C, Moliterno DJ, Armstrong PW, Van de Werf F, et al. Thrombin-receptor antagonist vorapaxar in acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. (2012) 366:20–33. 10.1056/NEJMoa1109719 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Uphaus T, Richards T, Weimar C, Neugebauer H, Poli S, Weissenborn K, et al. Revacept, an inhibitor of platelet adhesion in symptomatic carotid stenosis: a multicenter randomized phase ii trial. Stroke. (2022) 2022:Strokeaha121037006. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.037006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Voors-Pette C, Lebozec K, Dogterom P, Jullien L, Billiald P, Ferlan P, et al. Safety and tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of ACT017, an antiplatelet GPVI (Glycoprotein VI) Fab. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2019) 39:956–64. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.312314 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Abdulsattar Y, Ternas T, Garcia D. Vorapaxar: targeting a novel antiplatelet pathway. P T. (2011) 36:564–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Li S, Tarlac V, Hamilton JR. Using PAR4 inhibition as an anti-thrombotic approach: why, how, and when? Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:5629. 10.3390/ijms20225629 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ridker PM, Everett BM, Thuren T, MacFadyen JG, Chang WH, Ballantyne C, et al. Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:1119–31. 10.1056/NEJMoa1707914 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vaidya K, Tucker B, Kurup R, Khandkar C, Pandzic E, Barraclough J, et al. Colchicine inhibits neutrophil extracellular trap formation in patients with acute coronary syndrome after percutaneous coronary intervention. J Am Heart Assoc. (2021) 10:e018993. 10.1161/JAHA.120.018993 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Silvis MJM, Fiolet ATL, Opstal TSJ, Dekker M, Suquilanda D, Zivkovic M, et al. Colchicine reduces extracellular vesicle NLRP3 inflammasome protein levels in chronic coronary disease: a LoDoCo2 biomarker substudy. Atherosclerosis. (2021) 334:93–100. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.08.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nidorf SM, Fiolet ATL, Mosterd A, Eikelboom JW, Schut A, Opstal TSJ, et al. Colchicine in patients with chronic coronary disease. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:1838–47. 10.1056/NEJMoa2021372 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fiolet ATL, Silvis MJM, Opstal TSJ, Bax WA, van der Horst FAL, Mosterd A, et al. Short-term effect of low-dose colchicine on inflammatory biomarkers, lipids, blood count and renal function in chronic coronary artery disease and elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. PLoS ONE. (2020) 15:e0237665. 10.1371/journal.pone.0237665 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tardif JC, Kouz S, Waters DD, Bertrand OF, Diaz R, Maggioni AP, et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:2497–505. 10.1056/NEJMoa1912388 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Martinez GJ, Celermajer DS, Patel S. The NLRP3 inflammasome and the emerging role of colchicine to inhibit atherosclerosis-associated inflammation. Atherosclerosis. (2018) 269:262–71. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.12.027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pennings GJ, Reddel CJ, Traini M, Campbell H, Chen V, Kritharides L. Colchicine inhibits ROS generation in response to glycoprotein VI stimulation. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:11965. 10.1038/s41598-021-91409-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Opstal TSJ Hoogeveen RM Fiolet ATL Silvis MJM The The SHK Bax WA . Colchicine attenuates inflammation beyond the inflammasome in chronic coronary artery disease: a lodoco2 proteomic substudy. Circulation. (2020) 142:1996–8. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.050560 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chiarito M, Stefanini GG. Antiplatelet therapy for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: challenging the certainties. Lancet. (2021) 397:2443–4. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01120-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jourdi G, Godier A, Lordkipanidze M, Marquis-Gravel G, Gaussem P. Antiplatelet therapy for atherothrombotic disease in 2022-from population to patient-centered approaches. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:805525. 10.3389/fcvm.2022.805525 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mehta SR, Yusuf S, Peters RJ, Bertrand ME, Lewis BS, Natarajan MK, et al. Effects of pretreatment with clopidogrel and aspirin followed by long-term therapy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: the PCI-CURE study. Lancet. (2001) 358:527–33. 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05701-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Steinhubl SR, Berger PB, Mann III JT, Fry ETA, DeLago A, Wilmer C, et al. Early and sustained dual oral antiplatelet therapy following percutaneous coronary interventiona randomized controlled trial. JAMA. (2002) 288:2411–20. 10.1001/jama.288.19.2411 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tantry US, Bonello L, Aradi D, Price MJ, Jeong YH, Angiolillo DJ, et al. Consensus and update on the definition of on-treatment platelet reactivity to adenosine diphosphate associated with ischemia and bleeding. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2013) 62:2261–73. 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wiviott SD, Braunwald E, McCabe CH, Montalescot G, Ruzyllo W, Gottlieb S, et al. Prasugrel versus clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. (2007) 357:2001–15. 10.1056/NEJMoa0706482 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Price MJ, Berger PB, Teirstein PS, Tanguay JF, Angiolillo DJ, Spriggs D, et al. Standard- vs. high-dose clopidogrel based on platelet function testing after percutaneous coronary intervention: the GRAVITAS randomized trial. JAMA. (2011) 305:1097–105. 10.1001/jama.2011.290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cayla G, Cuisset T, Silvain J, Leclercq F, Manzo-Silberman S, Saint-Etienne C, et al. Platelet function monitoring to adjust antiplatelet therapy in elderly patients stented for an acute coronary syndrome (ANTARCTIC): an open-label, blinded-endpoint, randomised controlled superiority trial. Lancet. (2016) 388:2015–22. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31323-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Collet JP, Cuisset T, Rangé G, Cayla G, Elhadad S, Pouillot C, et al. Bedside monitoring to adjust antiplatelet therapy for coronary stenting. N Engl J Med. (2012) 367:2100–9. 10.1056/NEJMoa1209979 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Leunissen TC, Wisman PP, van Holten TC, de Groot PG, Korporaal SJ, Koekman AC, et al. The effect of P2Y12 inhibition on platelet activation assessed with aggregation- and flow cytometry-based assays. Platelets. (2016) 2016:1–9. 10.1080/09537104.2016.1246713 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Aradi D, Storey RF, Komócsi A, Trenk D, Gulba D, Kiss RG, et al. Expert position paper on the role of platelet function testing in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Eur Heart J. (2014) 35:209–15. 10.1093/eurheartj/eht375 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sibbing D, Aradi D, Jacobshagen C, Gross L, Trenk D, Geisler T, et al. Guided de-escalation of antiplatelet treatment in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (TROPICAL-ACS): a randomised, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet. (2017) 390:1747–57. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32155-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gurbel PA, Becker RC, Mann KG, Steinhubl SR, Michelson AD. Platelet function monitoring in patients with coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2007) 50:1822–34. 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.07.051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fontana P, Roffi M, Reny JL. Platelet function test use for patients with coronary artery disease in the early 2020s. J Clin Med. (2020) 9:194. 10.3390/jcm9010194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Goebel S, Li Z, Vogelmann J, Holthoff HP, Degen H, Hermann DM, et al. The GPVI-Fc fusion protein Revacept improves cerebral infarct volume and functional outcome in stroke. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e66960. 10.1371/journal.pone.0066960 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Clark JC, Neagoe RAI, Zuidscherwoude M, Kavanagh DM, Slater A, Martin EM, et al. Evidence that GPVI is expressed as a mixture of monomers and dimers, and that the D2 domain is not essential for GPVI activation. Thromb Haemost. (2021) 121:1435–47. 10.1055/a-1401-5014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chen H, Locke D, Liu Y, Liu C, Kahn ML. The platelet receptor GPVI mediates both adhesion and signaling responses to collagen in a receptor density-dependent fashion. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:3011–9. 10.1074/jbc.M109714200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nieswandt B, Brakebusch C, Bergmeier W, Schulte V, Bouvard D, Mokhtari-Nejad R, et al. Glycoprotein VI but not alpha2beta1 integrin is essential for platelet interaction with collagen. EMBO J. (2001) 20:2120–30. 10.1093/emboj/20.9.2120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chen H, Kahn ML. Reciprocal signaling by integrin and nonintegrin receptors during collagen activation of platelets. Mol Cell Biol. (2003) 23:4764–77. 10.1128/MCB.23.14.4764-4777.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ollivier V, Syvannarath V, Gros A, Butt A, Loyau S, Jandrot-Perrus M, et al. Collagen can selectively trigger a platelet secretory phenotype via glycoprotein VI. PLoS ONE. (2014) 9:e104712. 10.1371/journal.pone.0104712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bigalke B, Geisler T, Stellos K, Langer H, Daub K, Kremmer E, et al. Platelet collagen receptor glycoprotein VI as a possible novel indicator for the acute coronary syndrome. Am Heart J. (2008) 156:193–200. 10.1016/j.ahj.2008.02.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bigalke B, Langer H, Geisler T, Lindemann S, Gawaz M. Platelet glycoprotein VI: a novel marker for acute coronary syndrome. Seminars Thromb Hemostasis. (2007) 33:179–84. 10.1055/s-2007-969032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bigalke B, Haap M, Stellos K, Geisler T, Seizer P, Kremmer E, et al. Platelet glycoprotein VI (GPVI) for early identification of acute coronary syndrome in patients with chest pain. Thromb Res. (2010) 125:e184–9. 10.1016/j.thromres.2010.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Qayyum R, Becker DM, Yanek LR, Faraday N, Vaidya D, Mathias R, et al. Greater collagen-induced platelet aggregation following cyclooxygenase 1 inhibition predicts incident acute coronary syndromes. Clin Transl Sci. (2015) 8:17–22. 10.1111/cts.12195 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Loyau S, Dumont B, Ollivier V, Boulaftali Y, Feldman L, Ajzenberg N, et al. Platelet glycoprotein VI dimerization, an active process inducing receptor competence, is an indicator of platelet reactivity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2012) 32:778–85. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.241067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Miura Y, Takahashi T, Jung SM, Moroi M. Analysis of the interaction of platelet collagen receptor glycoprotein VI (GPVI) with collagen. A dimeric form of GPVI, but not the monomeric form, shows affinity to fibrous collagen. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:46197–204. 10.1074/jbc.M204029200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Massberg S, Konrad I, Bultmann A, Schulz C, Munch G, Peluso M, et al. Soluble glycoprotein VI dimer inhibits platelet adhesion and aggregation to the injured vessel wall in vivo. FASEB J. (2004) 18:397–9. 10.1096/fj.03-0464fje [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Induruwa I, McKinney H, Kempster C, Thomas P, Batista J, Malcor JD, et al. Platelet surface receptor glycoprotein VI-dimer is overexpressed in stroke: the glycoprotein VI in stroke (GYPSIE) study results. PLoS ONE. (2022) 17:e0262695. 10.1371/journal.pone.0262695 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gardiner EE, Arthur JF, Kahn ML, Berndt MC, Andrews RK. Regulation of platelet membrane levels of glycoprotein VI by a platelet-derived metalloproteinase. Blood. (2004) 104:3611–7. 10.1182/blood-2004-04-1549 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Al-Tamimi M, Gardiner EE, Thom JY, Shen Y, Cooper MN, Hankey GJ, et al. Soluble glycoprotein VI is raised in the plasma of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. (2011) 42:498–500. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.602532 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Reddel CJ, Pennings GJ, Chen VM, Gnanenthiran S, Kritharides L. Colchicine as a modulator of platelet function: a systematic review. Seminars Thromb Hemostasis. (2022) 48:552–67. 10.1055/s-0042-1749660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wittels E, Israel A, Karpatkin S. Evidence for colchicine-dependent protease activity in human platelets. Thromb Res. (1981) 24:215–21. 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90091-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Shah B, Allen N, Harchandani B, Pillinger M, Katz S, Sedlis SP, et al. Effect of colchicine on platelet-platelet and platelet-leukocyte interactions: a pilot study in healthy subjects. Inflammation. (2016) 39:182–9. 10.1007/s10753-015-0237-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Menche D, Israel A, Karpatkin S. Platelets and microtubules. Effect of colchicine and D2O on platelet aggregation and release induced by calcium ionophore A23187. J Clin Invest. (1980) 66:284–91. 10.1172/JCI109855 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Andrews RK, Arthur JF, Gardiner EE. Targeting GPVI as a novel antithrombotic strategy. J Blood Med. (2014) 5:59–68. 10.2147/JBM.S39220 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rivera J, Lozano ML, Navarro-Nunez L, Vicente V. Platelet receptors and signaling in the dynamics of thrombus formation. Haematologica. (2009) 94:700–11. 10.3324/haematol.2008.003178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Arthur JF, Qiao J, Shen Y, Davis AK, Dunne E, Berndt MC, et al. ITAM receptor-mediated generation of reactive oxygen species in human platelets occurs via Syk-dependent and Syk-independent pathways. J Thromb Haemost. (2012) 10:1133–41. 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04734.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kuntamukkula MS, Moake JL, McIntire LV, Cimo PL. Effects of colchicine and vinblastine on platelet contractility and release. Thromb Res. (1982) 26:329–39. 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90251-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.De Rosa R, Piscione F, Galasso G, De Servi S, Savonitto S. Antiplatelet therapy in very elderly and comorbid patients with acute coronary syndromes. J Geriatr Cardiol. (2019) 16:103–13. 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2019.02.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kasjanovová D, Baláz V. Age-related changes in human platelet function in vitro. Mech Ageing Dev. (1986) 37:175–82. 10.1016/0047-6374(86)90074-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Cirillo P, Taglialatela V, Pellegrino G, Morello A, Conte S, Di Serafino L, et al. Effects of colchicine on platelet aggregation in patients on dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel. J Thromb Thrombolysis. (2020) 50:468–72. 10.1007/s11239-020-02121-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Xiao ZH, Theroux P. Clopidogrel inhibits platelet-leukocyte interactions and thrombin receptor agonist peptide-induced platelet activation in patients with an acute coronary syndrome. J Am College Cardiol. (2004) 43:1982–8. 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.10.071 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Denorme F, Rondina MT. Targeting glycoprotein VI for thromboembolic disorders. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2019) 39:839–40. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312621 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yeh JJ, Kuo IL, Yip HT, Hsueh MY, Hsu CY, Kao CH. Effects of colchicine use on ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke risk in diabetic patients with and without gout. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:9195. 10.1038/s41598-022-13133-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Masson W, Lobo M, Molinero G, Masson G, Lavalle-Cobo A. Role of colchicine in stroke prevention: an updated meta-analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2020) 29:104756. 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104756 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Katsanos AH, Palaiodimou L, Price C, Giannopoulos S, Lemmens R, Kosmidou M, et al. Colchicine for stroke prevention in patients with coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Neurol. (2020) 27:1035–8. 10.1111/ene.14198 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Onselaer MB, Nagy M, Pallini C, Pike JA, Perrella G, Quintanilla LG, et al. Comparison of the GPVI inhibitors losartan and honokiol. Platelets. (2020) 31:187–97. 10.1080/09537104.2019.1585526 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Zheng TJ, Lofurno ER, Melrose AR, Lakshmanan HHS, Pang J, Phillips KG, et al. Assessment of the effects of Syk and BTK inhibitors on GPVI-mediated platelet signaling and function. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2021) 320:C902–C15. 10.1152/ajpcell.00296.2020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zhou J, Yang RP, Song W, Xu HM, Wang YH. Antiplatelet activity of tussilagone via inhibition of the GPVI downstream signaling pathway in platelets. Front Med. (2020) 7:380. 10.3389/fmed.2020.00380 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.