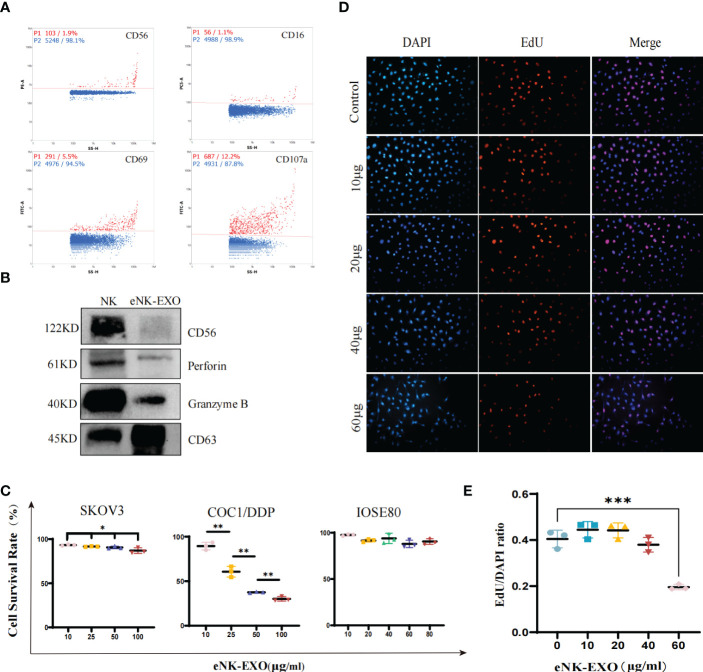
Figure 2.
Functional characterization of eNK-EXO in vitro. (A) Expression of eNK-EXO surface markers CD56, CD16, CD69 and CD107a by NanoFCM. Red dots represent positive signals. (B) Western blot analysis of CD56 (122KD), perforin (61KD) and GranzymeB (40KD) expression. NK cell lysate was used as control. (C) CCK-8 assay results of eNK-EXO against SKOV3, COC1/DDP and IOSE80 cells (n=3, mean ± SEM, t-test, *p< 0.05, **p< 0.01). (D, E) EdU assay results of eNK-EXO against SKOV3 (20×, scale bar = 100 µm). Red signals represent newly proliferating cells, whose proportion was quantified and shown (n=3, mean ± SEM, ***p< 0.001) (E).