Scheme 2. Proposed Model of Hybrid Vector Formulation and Assemblya.
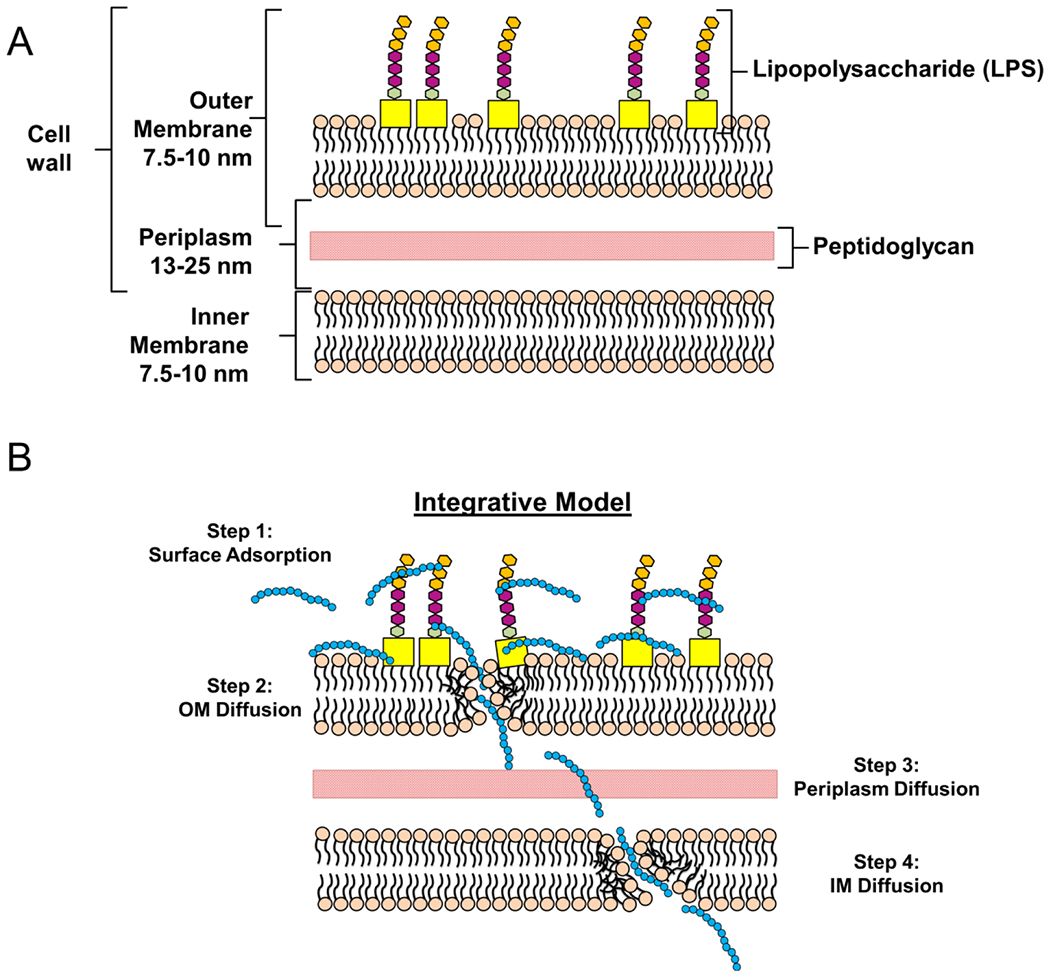
a(A) Layout of a normal cell wall of a Gram-negative bacterium. (B) The proposed hybrid formation model proceeds in four steps. First, polymer is adsorbed to the bacterial surface through charge–charge interaction (Step 1). Afterwards, the polymer diffuses slowly through the outer membrane (OM) while simultaneously compromising the structural integrity (Step 2). In the latter steps, the polymer chains diffuse slowly through the periplasmic space (Step 3) before subsequent integration and diffusion through the bacterial inner membrane (IM; Step 4). Taken together, these membrane disruptive steps are hypothesized to release internal bacterial cargo (i.e., DNA and protein) into the external periphery.
