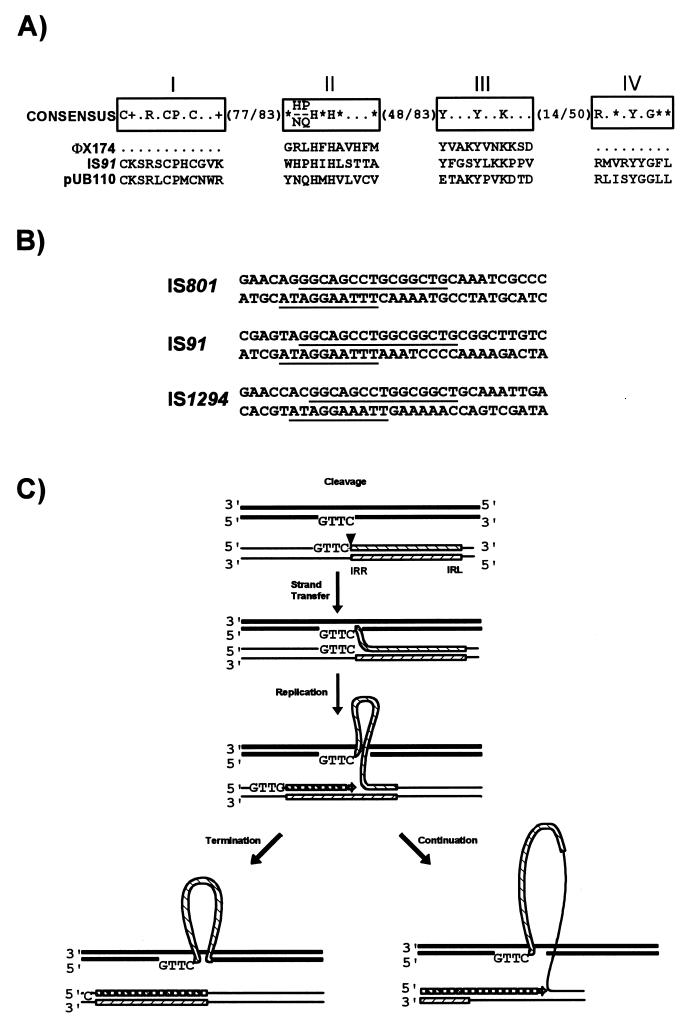
FIG. 15.
IS91 family. (A) Comparison of the primary Tpase sequence with related single-strand replicases. The four conserved regions are boxed and labelled I to IV. They are separated by various numbers of nonconserved amino acids as indicated. In addition to the standard one-letter amino acid code, + and ∗ represent basic and hydrophobic amino acids, respectively. IS91 is compared to bacteriophage φX174 and plasmid pUB110 replication proteins. (B) Transposon ends. Highly conserved sequences within the termini are underlined. The upper sequence in each pair represents the left end, and the lower sequence represents the right end. (C) Proposed rolling-circle mechanism for IS91 transposition. IS91 is shown as a hatched box with left and right termini, vector DNA is shown as a fine line, and target DNA is shown as a heavy line. Initial cleavage (vertical arrowhead) occurs at IRR and is followed by strand transfer to the conserved target sequence. Replication of the displaced strand in the donor DNA then takes place with priming from the liberated 3′ donor end. The left-hand pathway shows the result of correct cleavage and termination at the right extremity of the element. The right-hand pathway shows the result of progression through the termination signal and continuation into neighboring DNA of the donor molecule.