Figure 4.
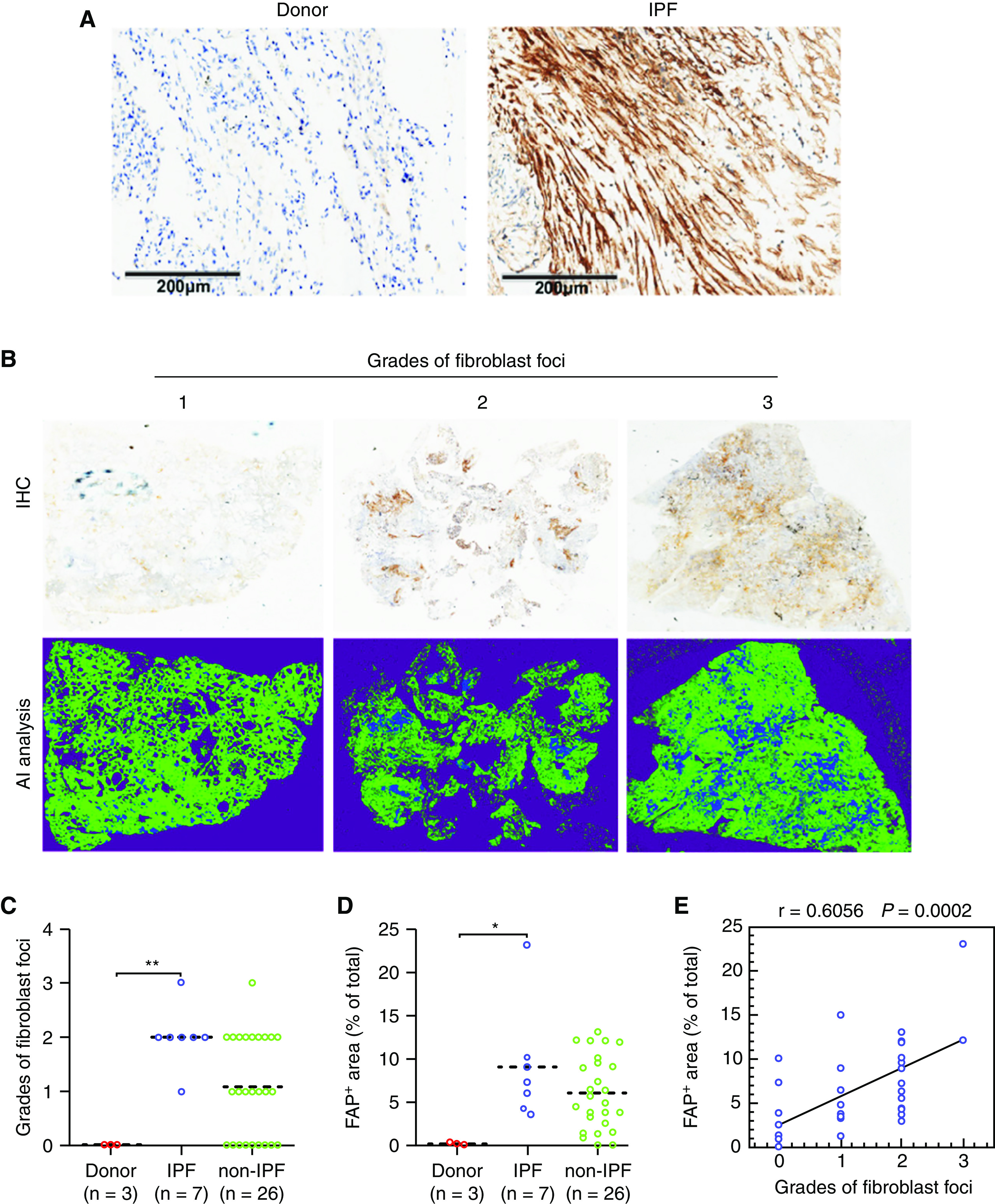
Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) expression in lung biopsies of patients with and without idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The lung biopsy tissue sections of IPF (n = 7) and non-IPF interstitial lung disease (ILD) (n = 26) were subjected to immunohistochemical staining of FAP. (A) Representative higher magnification immunohistochemistry images for FAP expression in donors and patients with IPF. Scale bars, 200 μm. (B) Representative immunohistochemistry images for patients with ILD with different grades of fibroblast foci (+, ++, and +++). The above columns indicate panorama images of original immunohistochemistry for the whole slide images, and the below columns indicate the positive signal extraction (blue) by artificial intelligence analysis. The grades of (C) fibroblast foci and (D) percentages of FAP-positive areas within the WSI for donors, patients with ILD and IPF, and patients with ILD but without IPF. (E) Correlation between the percentages of FAP-positive areas and the grades of fibroblast foci for patients (n = 33), including IPF and non-IPF, r = 0.6056; P = 0.0002, data are shown in correlation plots. The dashed line is a median. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
