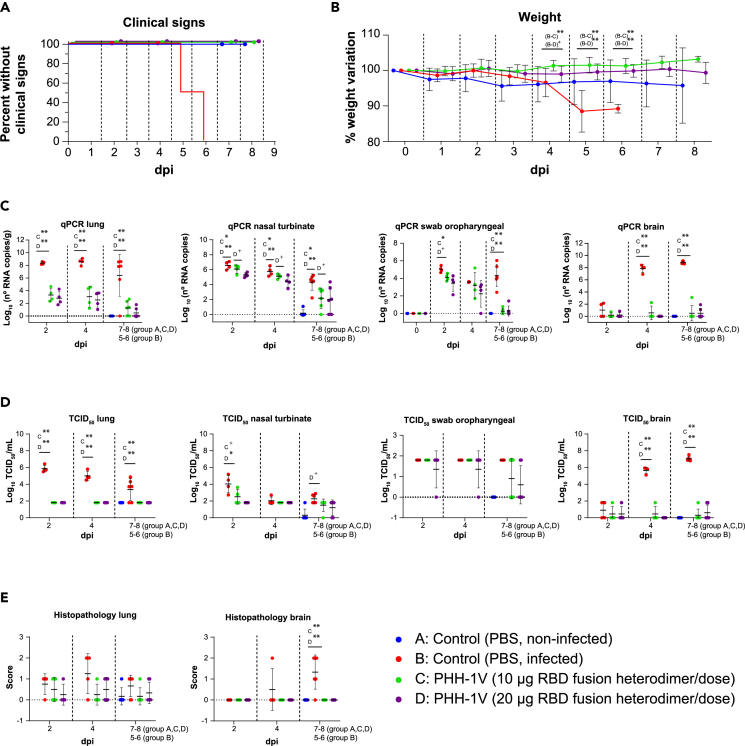
Figure 5.
Protective efficacy of PHH-1V vaccine in K18-hACE2 mice on SARS-CoV-2 challenge
Group A (n = 8, 4F + 4M), group B (n = 18, 9F + 9M), group C (n = 18, 9F + 9M), and group D (n = 18, 9F + 9M).
(A) Survival curves for groups of immunized K18-hACE2 mice with PHH-1V vaccine and control groups. Survival analysis (Kaplan-Meier estimates and logrank test to compare groups) was performed to study differences in time to/before clinical signs and mortality.
(B) Mean weight change after SARS-CoV-2 challenge calculated as a percentage of the pre-challenge weight in K18-hACE2 mice. A linear mixed effects model on the body weight change data was performed considering groups B, C and D. Points represent the average weight variation in each group and error bars depict a ± SD interval.
(C) SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR (number of copies) in the lungs, nasal turbinate, oropharyngeal swabs and brain collected from challenged animals.
(D) Viral titers were determined using a standard TCID50 assay on positive samples of RT-qPCR (in some exceptional cases, RT-qPCR and viral isolation were performed in parallel for logistical reasons). RT-qPCR-negative samples are represented as 0 TCID50/mL. The detection limit was set at 1.8 TCID50/mL.
(E) Histopathological analyses from the lungs and brain were determined for all animals. For each tissue sample, lesions were classified as follows: multifocal broncho-interstitial pneumonia; multifocal lymphoplasmacytic rhinitis; multifocal lymphoplasmacytic meningoencephalitis; and multifocal mononuclear inflammatory infiltrates within and around muscular fibers. Lesions were evaluated with the following score: 0 (no lesion); 1 (mild lesion); 2 (moderate lesion); and 3 (severe lesion). Samples of groups A, C and D correspond to 2 (D37), 4 (D39) and 7 dpi (D42 for males) or 8 dpi (D43 for females); samples of group B were taken 2 (D37), 4 (D39), and 5 dpi (D40; n = 3) or 6 dpi (D41; n = 3), when animals reached the endpoint criteria. GLS models or Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s post-hoc tests were employed for the analysis of the RT-qPCR, TCID50 and histopathological data depending on verification of assumptions. Each data point represents an individual mouse value, with bars representing the mean ± SD. Statistically significant differences between groups are indicated with a line on top of each group: ∗p<0.05; ∗∗p<0.01; +0.05<p<0.1. DPI: days post infection. See also Figures S1–S4.