Figure 1. Limited Proteolysis-Mass Spectrometry (LiP-MS) Experimental and Analytical Workflow.
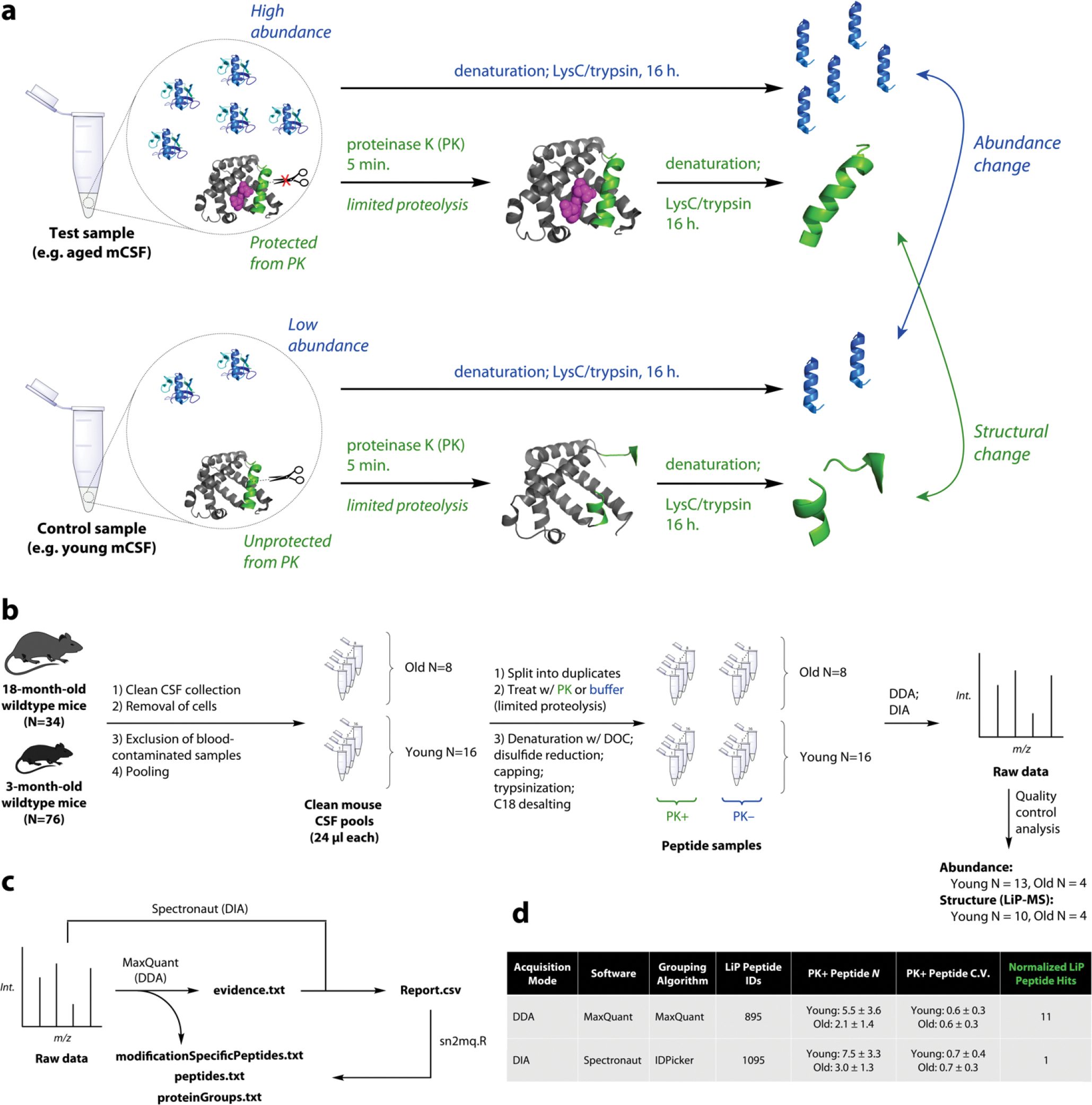
a. Schematic of limited proteolysis-mass spectrometry (LiP-MS). In LiP-MS, proteins in their native state are treated briefly with a nonspecific protease such as proteinase K (PK) which induces non-tryptic cleavages. The resulting peptides’ intensities relative to protein abundances reflect changes in the chemical structures or states of proteins.
b. Clean CSF was collected from 76 young and 34 old B6 wildtype mice. Cells were removed and samples were put through multiple quality control steps to remove contaminated samples. 24-μl pools were generated, each from a distinct combination of individuals, and LiP-MS was performed in both data-dependent acquisition (DDA) and data-independent acquisition (DIA) mode. Quality control analysis of raw and searched data resulted in final sample sizes 13, 10, and 4 for aging analysis.
c. Raw DDA data were searched with MaxQuant in order to generate a quantitative DDA dataset (.txt files) and to generate a DIA library. Raw DIA data were analyzed with this library in Spectronaut and the output (Report.csv) was converted using an R script to match the format of the MaxQuant output.
d. Although DIA performed better by fundamental metrics than DDA, DIA yielded fewer raw hits when the data were analyzed in the traditional manner, leading us to consider whether raw hits were genuine. Note: hardware malfunctions resulted in some unusable data files, resulting in lower N for processed data.
