Figure 3. Aging-Associated Changes in Structure Revealed by LiP-TeCS.
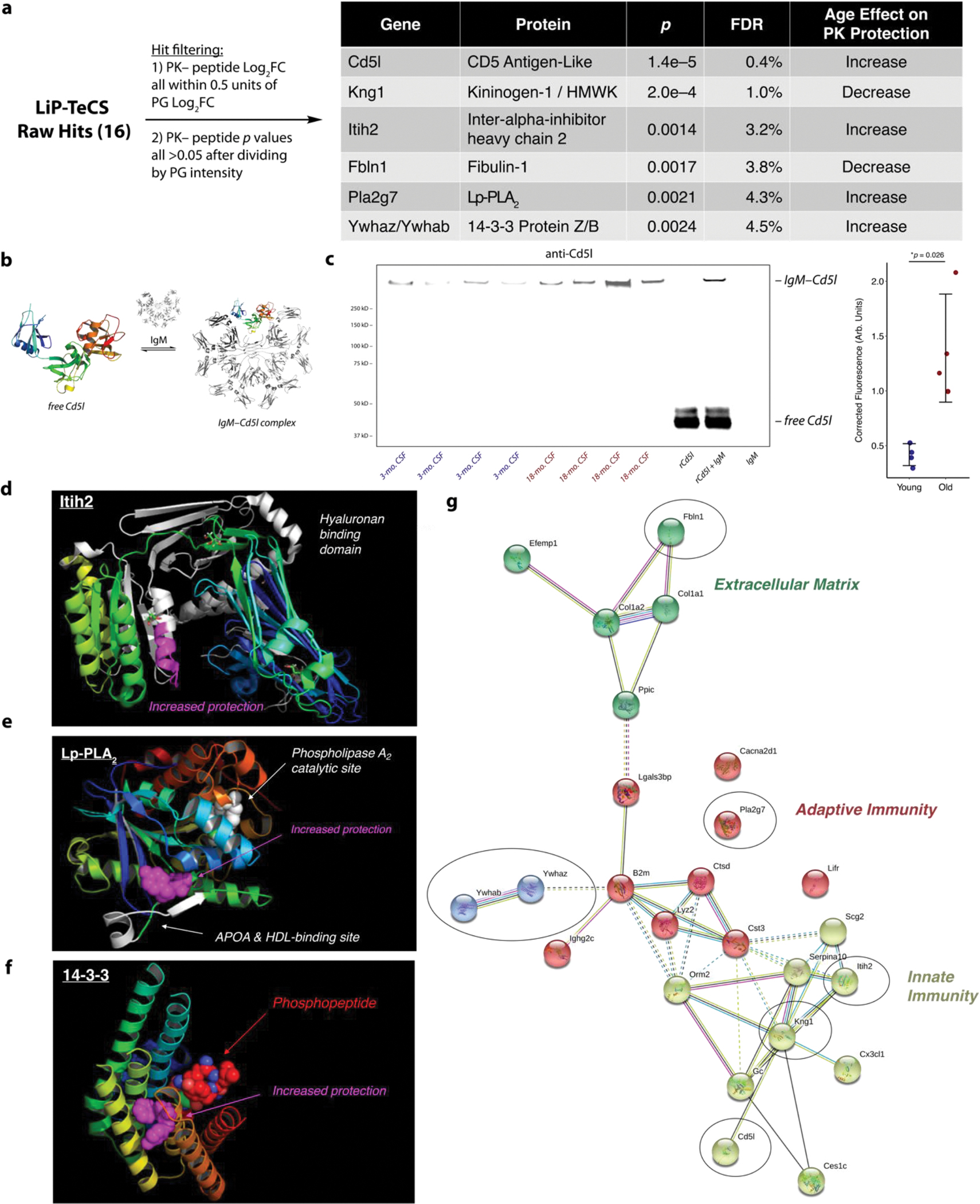
a. High-confidence LiP-TeCS hits.
b. Structures of free Cd5l and covalent Cd5l-IgM, known to coexist in plasma.
c. Nonreducing Western blot (anti-mCd5l, R&D Systems AF2834) of N=4 young vs. N=4 old biologically distinct CSF pools. rCd5l = recombinant mouse Cd5l (R&D Systems 2834-CL). IgM = mouse IgM (ThermoFisher MGM00). Error bars: mean +/− standard deviation. P value: two-sided T test.
d. Significant Itih2 LiP site is located in the hyaluronan binding domain.
e. Significant LiP site in Pla2g7/Lp-PLA2 is located between the known binding site for apolipoprotein A (APOA) / high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and the catalytic site where phosphatidylcholine (PC) is converted to lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC).
f. Significant LiP site on 14-3-3 protein Z/B is in the binding site of phosphoproteins involved in signaling.
g. STRING network with abundance and LiP-TeCS hits. LiP-TeCS hits in black ovals. Cluster coloring by STRING algorithm.
