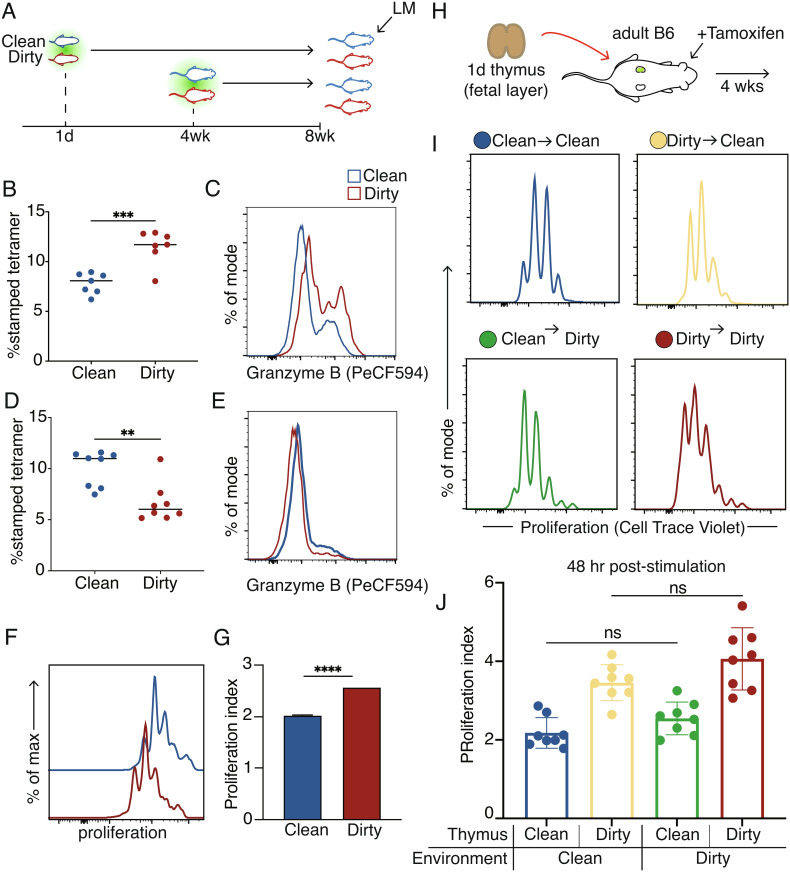
Fig. 3.
Fetal-derived cells in the dirty environment are more responsive to stimulation. (A) Approach to infect clean or dirty timestamp mice with Listeria. (B) The proportion of antigen-specific fetal-derived cells at 5 d post-LM infection. (C) Representative histogram showing Granzyme B production after infection in fetal-derived cells. (D) The proportion of antigen-specific adult-derived CD8+ T cells at 5 d post-LM infection. (E) Representative histogram showing Granzyme B production in adult-derived cells. (F) Representative histograms of proliferation peaks after aCD3/28 activation. (G) Division index of clean or dirty fetal-derived cells. (H) Experimental approach for kidney capsule thymic transplant surgeries. (I) Representative proliferation peaks 48 h after in vitro activation with aCD3/CD28. (J) Division index of fetal-derived cells after aCD3/28 stimulation. Data for B and D are ±SEM and are pooled from two independent experiments (n = 3–4 mice/group). Statistical significance for B and D was determined by Student’s t test. Statistical significance for J was determined by a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey multiple comparison posttest (ns = not significant, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005).