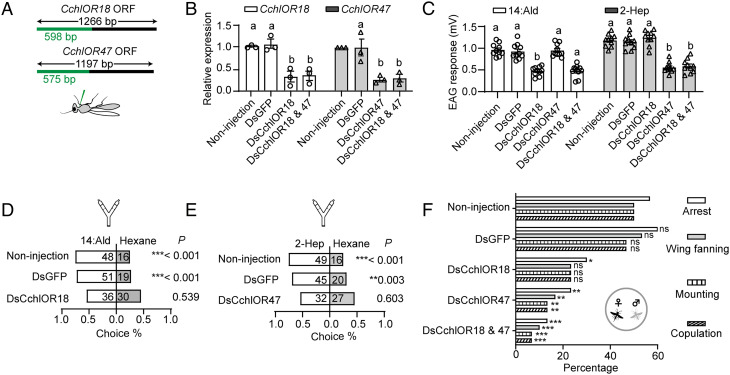
Fig. 4.
Knockdown of CchlOR18 and CchlOR47 attenuates antennal and behavioral responses to 14:Ald and 2-Hep. (A) Gene regions for dsRNAs synthesis. A gene fragment of 598 bp and 575 bp at the 5′-end of CchlOR18 and CchlOR47 was cloned as templates for dsRNAs synthesis. (B) qRT-PCR measurements to check the efficiency of CchlOR18 and CchlOR47 knockdown (n = 3). (C) EAG responses of the parasitoids defective in CchlOR18 and CchlOR47 versus the responses of two controls, non-injected and dsGFP injected wasps (n = 10). (D) Behavioral responses of non-injected, dsGFP injected, and dsCchlOR18 injected wasps to 1000 ng of 14:Ald. The parasitoids with CchlOR18 being knocked down lost the preference for 14:Ald. (E) Behavioral responses of non-injected, dsGFP injected, and dsCchlOR47 injected wasps to 1000 ng of 2-Hep. The parasitoids defective in CchlOR47 lost preference for 1000 ng of 2-Hep. (F) The percentage of males attempting to mate. Knocking down of CchlOR18 or CchlOR47 as well as both impaired the mating ability of males (n = 6). The different letters above the graphs indicate statistical differences. Note that each group contains five male wasps; therefore, totally 30 parasitoids were tested. Different letters above columns in panels B and C indicate significant differences tested by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by binomial test for panels D and E and by X2 test for panel F.