Figure 4.
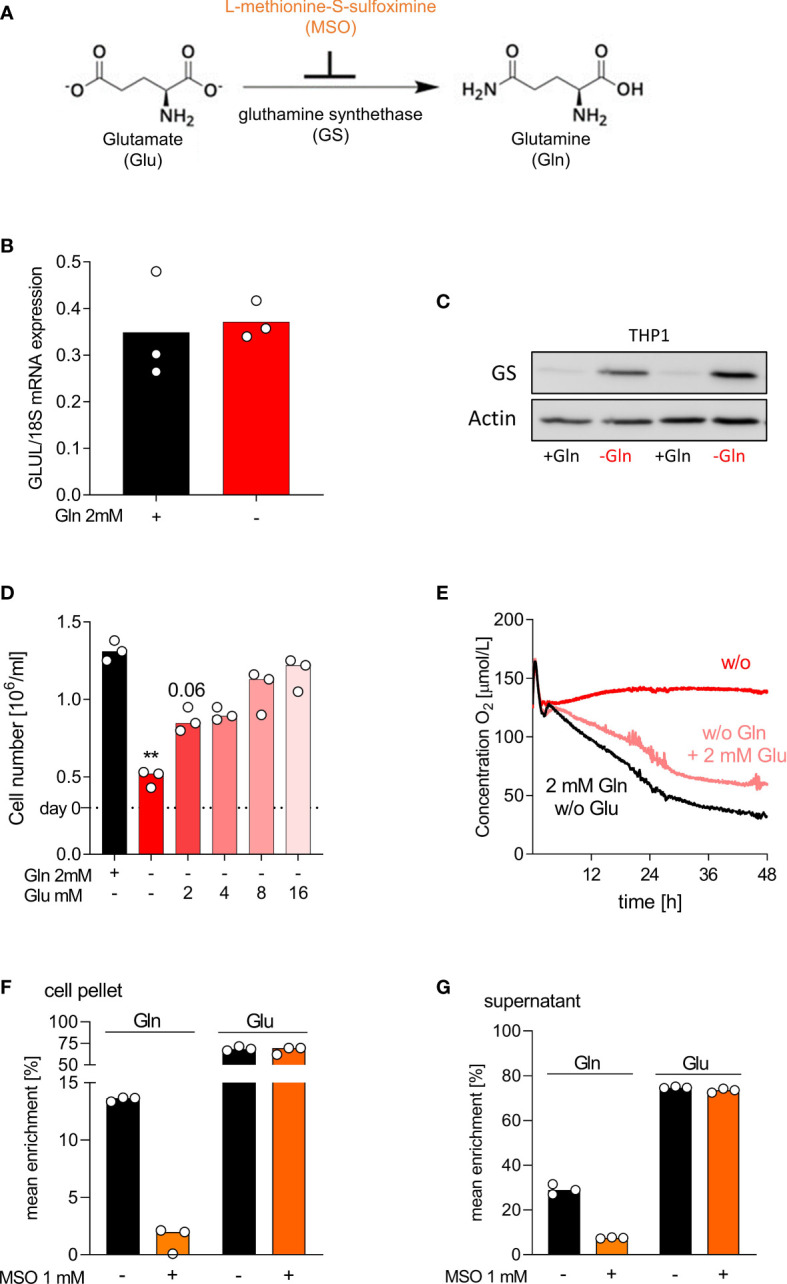
THP-1 adapt to glutamine-free conditions by upregulation of glutamine synthetase. (A) Schematic representation of Gln neogenesis; Glutamate (Glu) can be amidated to Gln by glutamine synthetase (GS). The enzyme GS is irreversibly inhibited by the substance L-methionine-S-sulfoximine (MSO). (B, C) THP-1 cells were cultured in presence or absence of 2 mM glutamine (Gln). (B) The mRNA expression of GLUL was determined by qPCR after 2 days and normalized to 18S mRNA. Shown are median values and single data points. Statistical significance was calculated using Wilcoxon’s matched pair signed rank test (no significance detected). (C) Western Blot analysis of GS in THP-1 after 2 days. (D) Cell yield of THP-1 was analyzed after 2 days of culture with or without 2 mM Gln or increasing Glu concentrations (2 mM, 4 mM, 8 mM, 16 mM). Shown are median values and single data points. Statistical significance was calculated using Friedman test with Dunn`s multiple comparison test (**p < 0.01). (E) Oxygen consumption was monitored in the absence (w/o, without) or presence of 2 mM Gln or 2 mM Glu using the PreSens technology (mean values, n = 3). (F, G) THP‐1 cells were incubated with 2 mM [13C5]glutamate in the presence or absence of 1 mM MSO for 24 h. After 24 h, cells were lysed and the mean enrichment of 13C in glutamate and glutamine were determined in cell pellets (F) and supernatants (G) by mass spectrometry. Shown are median values and single data points. Statistical significance was calculated using Wilcoxon’s matched pair signed rank test (no significance detected).
