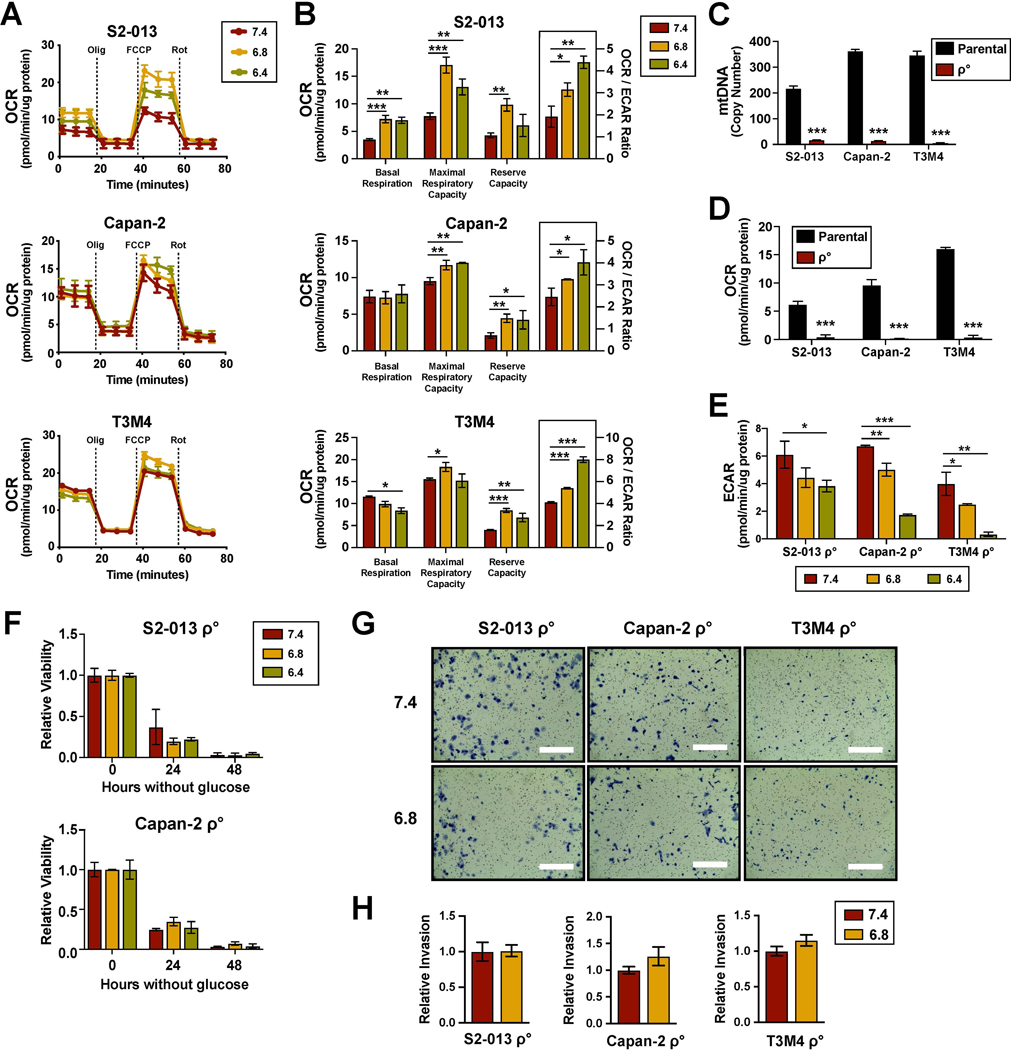
Figure 2. Mitochondrial respiration is required for increased invasion induced by acidic conditions.
(A) Oxygen consumption rates (ECAR) measured at baseline conditions and after sequential injections of oligomycin, FCCP, and rotenone using the Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer. (B) Parameters of mitochondrial respiration calculated from the OCR measurements (n=3). (C) Quantification of mitochondrial DNA copy number through qPCR of total DNA extract using genomic DNA as reference (n=3). (D) OCR measurements of ρ° cells and their parental counterparts (n=3). (E) ECAR measurements ρ° cells pre-cultured under indicated pHe conditions (n=3). (F) Relative viability of ρ° cells following glucose starvation compared to unstarved controls (n=3). (G) Representative images from Matrigel invasion assays with ρ° cells. Bar, 400μm. (H) Quantification of relative invasion (n=2). Data are shown as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.