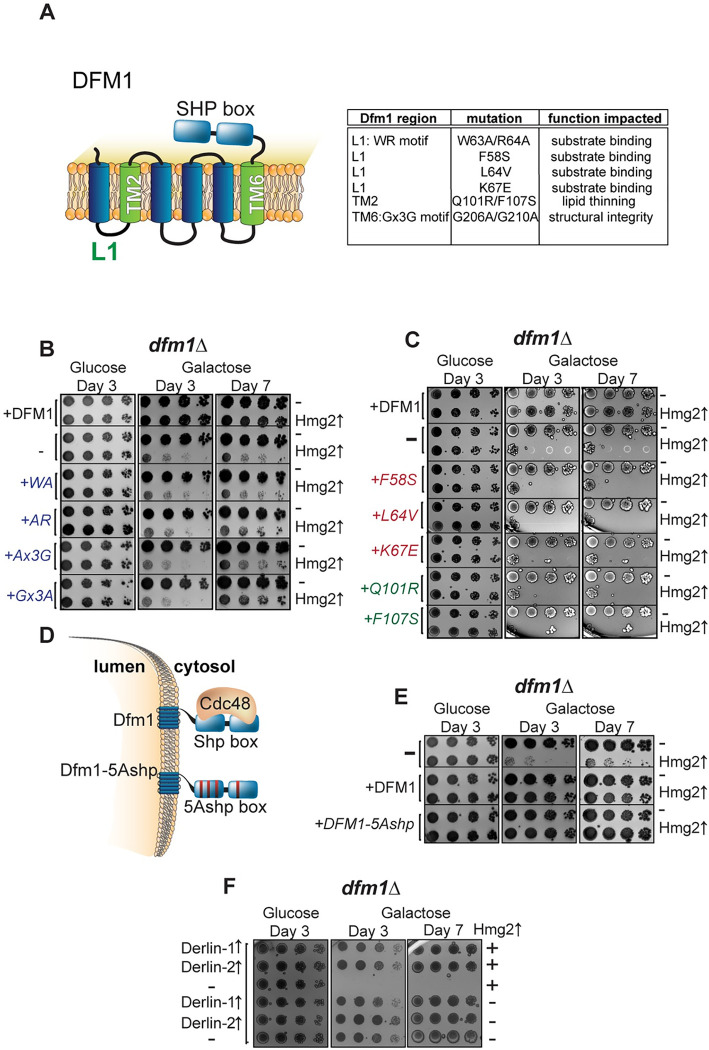
Fig 2. Dfm1 retrotranslocation defective mutants show differing abilities to restore growth.
(A) Depiction of Dfm1, which highlights L1, TM2, TM6, and its SHP box domain. The table indicates the Dfm1 region, amino acid mutation, and the corresponding function that is specifically impaired. All mutants have been previously identified as being required for retrotranslocation and when mutated did not restore growth in dfm1Δ cells expressing an integral membrane protein (GALpr-HMG2-GFP). (B) dfm1Δ cells with an add-back of either WT DFM1-HA, EV, DFM1-WA-HA, DFM1-AR-HA, DFM1-Ax3G-HA, or DFM1-Gx3A-HA containing either GALpr-HMG2-GFP or EV were compared for growth by dilution assay. Each strain was spotted 5-fold dilutions on glucose or galactose-containing plates to drive Hmg2-GFP overexpression, and plates were incubated at 30°C. (C) Dilution assay as described in (B) except using an add-back of either WT Dfm1-HA, EV, Dfm1-F57S-HA, Dfm1-L64V-HA, Dfm1-K67E-HA, Dfm1-Q101R-HA, or Dfm1-F107S-HA. (D) Depiction of Dfm1 and Dfm1-5Ashp. Dfm1 is an ER-localized membrane proteins with 6 TMDs. Both versions of Dfm1 have a cytoplasmic shp box, but the 5Ashp mutant is unable to recruit the cytosolic ATPase Cdc48. (E) Dilution assay as described in (B) except using add-back of either EV, WT DFM1-HA, or DFM1-5Ashp-HA mutant. (F) Dilution assay as described in (B) except with add-back of human Derlin-1-Myc or Derlin-2-Myc. All dilution growth assays were performed in 3 biological replicates and 2 technical replicates (N = 3). ER, endoplasmic reticulum; EV, empty vector; TMD, transmembrane domain.