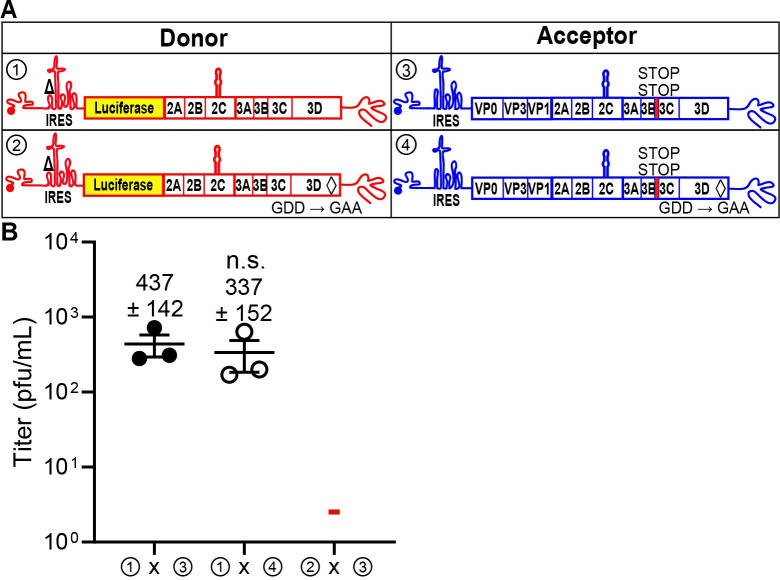
Fig 4. A 10-nt deletion in the IRES that is known to prevent translation recapitulates phenotypes observed with a deleted IRES.
(A) The donor RNA was engineered to contain a 10-nucleotide deletion (nt 185–189, nt 198–202) known to disrupt the IRES (referred to as ΔSLII-3) [40] with an active or an inactive RdRp. (B) Comparison of infectious virus produced between the indicated donor and acceptor RNAs with the specific modifications. Results show titer of recombinant virus (pfu/mL ± SEM; n = 3).—indicates that plaques were not detected (limit of detection: 2 pfu/mL). Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired, two-tailed t test (n.s. indicates not significant). Viral recombinants were recovered using a donor RNA containing the ΔSLII-3 and an active RdRp with the indicated acceptor RNAs (① x ③, ① x ④); viral recombinants were not recovered when the donor RNA contained ΔSLII-3 and encoded an inactive RdRp (② x ③). Numerical data provided as Supporting information (S1 Data). IRES, internal ribosome entry site; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.